
This is why you should sleep at the same time every night, according to experts
Scientists have revealed why people should head to sleep at the same time every night. A study by Kings College London which involved 1,000 adults, aimed to find whether "social jetlag" (the shift between sleep patterns on work days and free days) can have an impact on health. In doing so, researchers discovered that sleeping at the same time and a healthy diet could decrease the risk of disease. They found that even a 90-minute difference in the mid-point of sleep could impact the types of bacteria in the gut. They analysed participants' sleep, blood and stool samples, and logged everything they consumed in a food diary. Those with "social jetlag" (16 per cent) appeared to have a diet filled with potatoes, crisps, chips and sugary drinks. Other studies have suggested that social jetlag is linked to weight gain, illness and mental fatigue. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Dr Wendy Hall, senior author from King’s College London, said: "We know that major disruptions in sleep, such as shift work, can have a profound impact on your health. "This is the first study to show that even small differences in sleep timings across the week seems to be linked to differences in gut bacterial species. "Some of these associations were linked to dietary differences but our data also indicates that other, as yet unknown, factors may be involved. "We need intervention trials to find out whether improving sleep time consistency can lead to beneficial changes in the gut microbiome and related health outcomes." Kate Bermingham, study author and senior nutrition scientist at ZOE, said: "Sleep is a key pillar of health, and this research is particularly timely given the growing interest in circadian rhythms and the gut microbiome. "[Social jetlag] can encourage microbiota species which have unfavourable associations with your health," she continued. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-02 16:53

The 'doomed Phobos moon' is about the crash into Mars
When NASA’s Perseverance Rover observed an image from Mars of its moon Phobos eclipsing the Sun, it was a reminder that the astronomical body is doomed to crash into the planet. Phobos is the closest of Mars’ two moons and it is due to fall out of orbit relatively soon. When it does, it will either crash into the surface of the planet or break up completely. Before it does, it will drift ever closer to Mars at a relatively rapid rate. "Phobos is nearing Mars at a rate of six feet (1.8 meters) every hundred years; at that rate, it will either crash into Mars in 50 million years or break up into a ring," NASA says about the moon. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter A statement about the recently recorded eclipse states: "Scientists already know that Phobos is doomed. “The moon is getting closer to the Martian surface and is destined to crash into the planet in tens of millions of years. But eclipse observations from the surface of Mars over the last two decades have also allowed scientists to refine their understanding of Phobos’ slow death spiral." NASA's Perseverance Rover Sees Solar Eclipse on Mars www.youtube.com Mars is the subject of much scientific interest right now, especially after Nasa discovered “diverse organic matter” on the surface of the planet, which could change our understanding of the red planet and the search for life in the universe. The Perseverance rover made the discovery in the Jezero Crater on Mars and a number of different explanations for the existence of the material have been posited. The materials could have been formed when water and dust interacted, or was dropped onto the planet by dust or meteors. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-31 20:52

OceanGate founder now wants to send people to least hospitable planet in the galaxy
The co-founder of the OceanGate is now planning to send 1000 people to Venus despite the bad press the company has received following the doomed Titanic submersible trip in June which killed five people. Despite the tragedy, which saw the submersible implode killing everyone onboard, including the company's co-founder Stockton Rush, his colleague Guillermo Söhnlein is not deterred and has told Insider that he now has ambitions for space. According to Söhnlein he now wants to see 1000 people living on the surface of Venus, the hottest planet in the solar system, by 2050. The American businessman born in Argentina said: "I think it is less aspirational than putting a million people on the Martian surface by 2050. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter "You're absolutely right that when you talk about going to Venus, it would raise eyebrows outside the space industry. And it even raises eyebrows inside the space industry." "I think I've been driven to help make humanity a multi-planet species since I was 11 years old, I had this recurring dream of being the commander of the first Martian colony." This all sounds well and good and after all Elon Musk has similar aspirations for Mars but Venus is an odd one as at this moment in time its one of the least hospitable planets in the galaxy. Aside from being the hottest planet in the solar system, as mentioned, its atmosphere is made up of greenhouse gases and its clouds contain sulphuric acid which make Venus so hot that temperatures can reach 475 °C. Regardless of this, Söhnlein thinks it is "very doable" that a floating space station could withstand the harsh conditions on Venus but will likely be met with skepticism. Söhnlein's Humans2Venus project has been co-founded with researcher Khalid Al-Ali and will strive to develop technologies that will reduce launch costs and fund space projects without government money. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-30 16:15
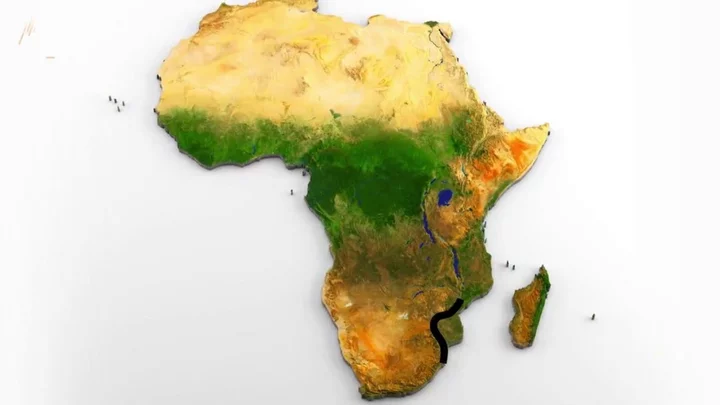
New ocean discovered that is beginning to split Africa in two
Since the break up of Pangea that formed the world, we have been taught that there are seven oceans. But now, scientists believe a brand new ocean is currently forming as the continent of Africa is slowly beginning to split in half. Researchers have found two large parts of the land within Africa have begun to separate and it's believed a whole new ocean will form in the divide. Africa is the second-largest continent in the world, with a landmass of more than 30 million square kilometres, and is also the second-most populous. Many of its 54 countries are landlocked, however for some that could be about to change. Geologists believe countries such as Uganda and Zambia could come to have their own coastlines if the two land masses continue to separate. In the peer-reviewed journal, Geophysical Research Letters, experts have confirmed that the split in the African continent is creating a way for a new ocean to form. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter Scientists have identified the exact location where the continent first started to split, very deep underground. The crack first began to appear in 2005 in Ethopia’s deserts. The crack is known as the East African Rift and is 35 miles long. The start is positioned at the meeting point of three tectonic plates which have been gradually pulling apart from each other. Christopher Moore, a Ph.D. doctoral student at the University of Leeds, told NBC News: “This is the only place on Earth where you can study how continental rift becomes an oceanic rift.” Moore and other researchers have used satellite radar to monitor the volcanic activity in East Africa as this is associated with tectonic shifts. Despite being able to monitor movement, the split is a very gradual process, and scientists believe it will take another 5 to 10 million years for the new ocean to fully form. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-29 23:57
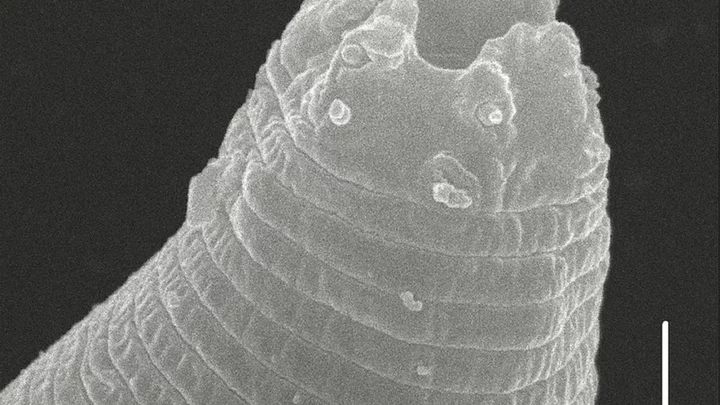

Experts resurrect parasite after 46,000 years in Siberian permafrost
Scientists have resurrected a parasite which has been dormant in the frozen permafrost of Siberia for 46,000 years. The microscopic creatures were first uncovered as part of a remarkable discovery back in 2018. At the time, researchers led by Anastasia Shatilovich found two of the worms in sub-zero temperatures in the soil. At first, it was previously thought that the creatures could stay in their slumber for just 40 years. However, it was later revealed that they could stay inactive for tens of thousands of years. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The creatures tend to shut down their systems when they are in unfavourable conditions. This means they won’t move or reproduce, and their metabolism stops. Carbon analysis has revealed that the worms – also known as nematodes – came from a prehistoric era. The developments could change the way experts approach bringing back other extinct species, too. During an analysis, the research team discovered the worms were Panagrolaimus kolymaensis - a species that was previously thought to be extinct. The scientists wrote in their paper: “Previously, we had shown that nematodes from the Siberian permafrost with morphologies consistent with the genera Panagrolaimus and Plectus could be reanimated thousands of years after they had been frozen. “Several viable nematode individuals were found in two of the more than 300 studied samples of permafrost deposits spanning different ages and genesis.” It’s not the only thing that scientists have recovered from permafrost, either. It was announced earlier this year that scientists are busy working on reviving 'zombie viruses’ that have been lying dormant for tens of thousands of years in Arctic conditions, and while it sounds absolutely terrifying, it could be important when it comes to protecting us all in the future. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-28 19:23

Scientists say people have the ability to 'smell' rain before it arrives
Ever wondered why people say they can smell rain before it rains? They are not pulling your leg - there is real science behind it. It is all because of petrichor, made up from the Greek words "petra", meaning stone, and '"ichor", which refers to the golden fluid that flows in the veins of the gods in their mythology. It basically means the the "smell of rain" with the phrase coined by Australian scientists Joy Bear and Richard Thomas in 1964. Jeff Weber, a meteorologist with the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research Unidata Program Center told the Mirror: "Petrichor is caused by oils derived from plants, primarily leaves, that accumulate over dry periods. These oils settle into soils or onto pavement over time and are released into the atmosphere by being disturbed by rainfall." According to the Met Office, the reason people claim to smell rain because it comes is because "when a higher humidity is experienced as a precursor to rain, the pores of rocks and soil become trapped with moisture forcing some of the oils to be released into the air". Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Despite some being released before it actually rains, the strongest smell is released during. This is when raindrops landing on soil "trap tiny air bubbles on the surface which then shoot upward" and "burst out of the drop throwing aerosols of scent into the air where they are then distributed by the wind". The smell is produced by a soil bacteria which releases a chemical called geosmin, which provides an "earthy", musky or fresh aroma. Before it rains, a person might be able to smell the scent of ozone, or O3, which is a naturally present gas in the atmosphere which gets its name from the Greek word 'ozein', or smell. It sometimes indicate that a storm is on the way because pockets of gas are pushed down to ground level by winds. This means that those who are sensitive to the smells will likely be able to pick them up. So now you know. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-27 23:23
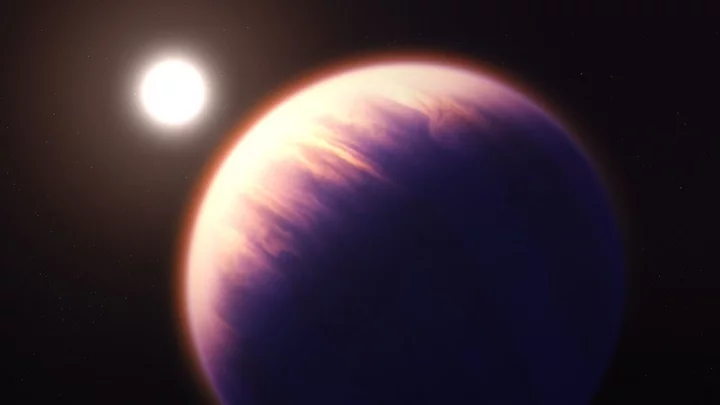

Scientists discover strange 'candyfloss' planet with fluffy atmosphere
Scientists have discovered one of the strangest exoplanets ever that is so light and fluffy that it is actually being compared to candyfloss (or cotton candy if you are American). The planet is called WASP-193b and is 1,232 light-years away and was discovered by researchers at the University of Liège in Belgium. The findings of their study, led by astronomer Khalid Barkaoui has been published on arXiv. The planet, which is believed to be a so-called gas giant is nearly 50 per cent bigger than Jupiter and is orbiting a Sun-like star named WASP-193, which the scientists believe is up to 6 billion years old. Although this star is slightly bigger than our sun it is still said to have the same temperature but compared to Earth, WASP-193b orbits its star just every 6.25 days. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter By studying the planet, Barkaoui and his team were able to determine that its density was around 0.059 grams per cubic centimetre. Earth's density per cubic centimetre for comparison, is 5.51 grams whereas candyfloss has a density of 0.05 grams. There are few other examples of a planet like this existing but its close proximity to a star may give an indication as to how it came to exist as its heat is likely to have warmed up the planet's puffy atmosphere, which is mostly made up of hydrogen and helium. This state of the planet is only set to last for around a few ten million years as the temperatures and winds emitted from the star are only likely to strip back the atmosphere further. Due to this scientists cannot fully recreate or determine what is causing WASP-193b's unique atmosphere but is it likely to be a continued source of study to try and determine the cause of this phenomenon. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-24 00:18
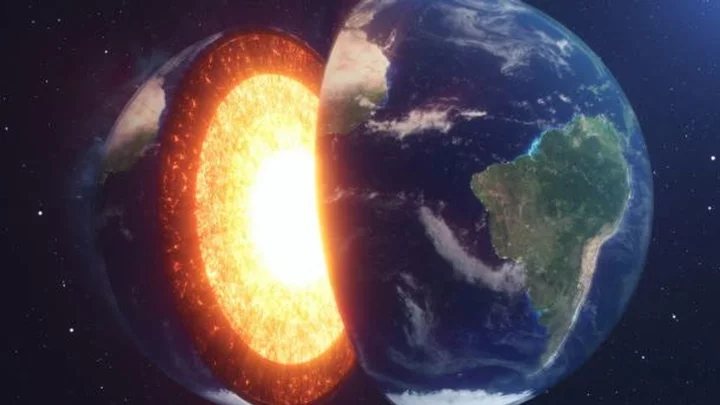

Hidden structure discovered in Earth's core could 'rewrite' scientist's understanding of the planet
Scientists think they have discovered a previously unknown hidden structure inside the Earth’s core that could change our understanding of our planet. In school, most of us were taught there are four main layers to the Earth’s structure: the crust, the mantle, the outer core and the inner core. What we know about the Earth’s insides has mostly derived from geologists’ knowledge and observations of volcanoes and seismic waves. But now, scientists believe that there may also be a whole extra layer hidden inside the inner core that no one knew about. Earth’s molten inner core is predicted to be around 5,000 degrees Celsius in temperature and scientists have calculated that it takes up around just 1 per cent of the planet’s total volume. The discovery of a potential fifth layer to the planet’s core came a few years ago when scientists used an algorithm to model thousands of scenarios of the inner core to observe the length of time it takes seismic waves to travel through Earth based on data by the International Seismological Centre. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter Scientists were able to analyse how different material properties within the inner core would affect seismic waves differently and found that some scenarios were certainly more likely than others. The algorithm showed how different materials altered the angle of seismic waves, leading them to hypothesise that there was a change of material somewhere in the inner core. Joanne Stephenson, an Australian National University geophysicist, explained: “We found evidence that may indicate a change in the structure of iron, which suggests perhaps two separate cooling events in Earth's history.” She continued: “The details of this big event are still a bit of a mystery, but we've added another piece of the puzzle when it comes to our knowledge of the Earth's inner core.” While their data isn’t conclusive, it does correlate with other similar studies that have looked into the anisotropy of the Earth’s inner core. Stephenson said: “It's very exciting - and might mean we have to re-write the textbooks!” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-23 20:52
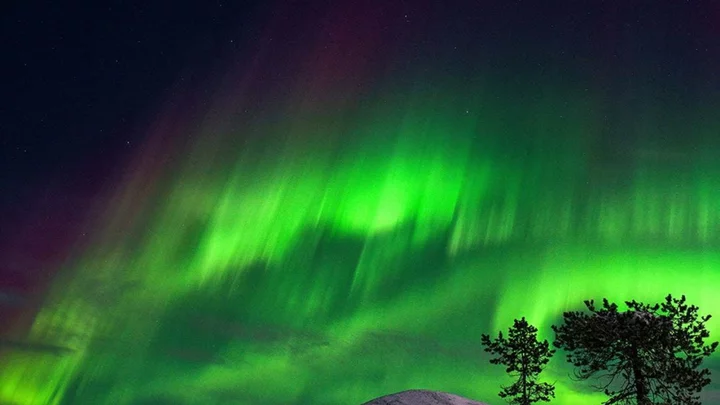

A cannibal solar storm will allow people in the UK to see the Northern Lights
The Northern Lights will be visible from the UK thanks to a large “cannibal” solar storm that is hitting the Earth. The aurora borealis (aka Northern Lights) are produced by when radiation from the Sun is deflected by the magnetic field of the Earth. Typically, the Northern Lights can be seen further north of the UK in the Nordic countries such as Iceland and Norway, as well as in northern parts of Canada. This is because when solar radiation hits the Earth, it is drawn to the Earth’s magnetic field, which runs north to south, and is directed towards to north and south poles. But, every now and then when there is a strong enough solar storm, they can also be seen further south in the UK because of the increased levels of solar radiation. From today (20 July), Brits stand a chance of catching a glimpse of the famous Nothern Lights once it turns dark. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Those in Scotland have the greatest chance of spotting the spectacle, however, they could also be viewed further south, but cloud cover and fewer hours of darkness mean it’s difficult to pinpoint cities with any great accuracy, says the Met Office. For the best chance to see the Northern Lights, experts recommend getting out of major cities. This is because, for the aurora borealis to be most visible, there must be minimal levels of light pollution which is not the case in built-up areas. The severity of the “cannibal” solar storm may be so strong that it disrupts radio signals and creates different weather patterns. Sean Elvidge, associate professor of space environment at the University of Birmingham, explained: “These storms manifest as major disturbances in Earth's magnetic field, potentially causing various space weather effects. “On one hand, they can result in radio blackouts, disrupting communication systems on our planet. On the other hand, these storms can produce awe-inspiring displays of natural beauty known as auroras.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-20 17:58

Who is Eunice Newton Foote? The scientist celebrated in today's Google Doodle
We talk about climate change and the devastating effects of greenhouse gases on a daily basis, yet many of us have never heard of Eunice Newton Foote. The American scientist was the first person to realise the alarming impact of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, all the way back in 1856. So, to mark what would have been her 204th birthday, Google has dedicated today’s Doodle to the environmental pioneer. Head to the search engine and you’ll find an 11-part slideshow explaining Foote’s most significant work. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It goes on to point out that her research was largely ignored for almost 100 years, and credits her with being the first person to “plant a seed of interest in the issue of climate change”. And for anyone wondering, her surname is no coincidence: her father was allegedly a distant relative of Sir Isaac Newton. In a blurb to its Doodle, Google points out that whilst science was Foote’s lifelong passion, she also dedicated time to campaigning for women’s rights. In 1848, she attended the first Woman’s Rights Convention in Seneca Falls, New York State and became the fifth signatory of the Declaration of Sentiments — which demanded equality for women in social and legal status. Back then, women were largely shunned from the scientific community, but this didn’t stop Foote from conducting experiments on her own. After placing mercury thermometers in glass cylinders, she noticed that the cylinder containing carbon dioxide heated up the most and took the longest to cool down. As a result, she became the first scientist to draw a connection between rising CO2 levels and the warming of the atmosphere. After publishing her findings, Foote wrote a second paper on atmospheric static electricity for the journal ‘Proceedings of the American Association for the Advancement of Science’. These were the first two physics studies to be published by a woman in the US, as Google notes. In 1856, a male scientist presented her work at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. This then lead to further experiments which uncovered what is now known as the Greenhouse effect. And whilst none of us relish the fact this phenomenon exists, we should be eternally grateful to Foote for flagging it to us, all those years ago. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-17 15:46
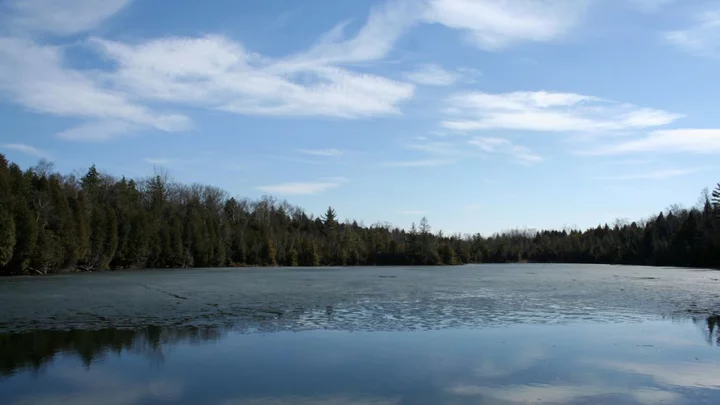

How one lake has captured the moment we changed the world forever
The floor of Crawford Lake in Ontario acts like a storybook, preserving Earth’s recent history in chronological order. Crawford Lake reveals the activities of local Iroquoian communities from the late 13th to 15th centuries, all the way through to the present day. This is because Crawford Lake is a meromictic lake, meaning that the dense bottom layer of water does not mix with the less dense upper layers. “The isolated bottom layer of water remains under disturbed, enabling the accumulation of clearly laminated valves which record precise information about the time during which they were deposited,” according to the Anthropocene Working Group. Experts have nominated Crawford Lake as representation for the start of the Anthropocene epoch, a proposed new geological era characterised by significant changes to the planet’s surface as a result of human behaviour. The Anthropocene is yet to be officially accepted as a unit of geologic time, but in 2016 a working group under the guidance of an International Commission on Stratigraphy subcommittee agreed that human behaviour has left scars so deep that they will remain evident even into the distant future. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter One of the most notable markers of the Anthropocene is the appearance of plutonium, a radioactive material that appeared in the mid-20th century as a result of hydrogen bomb tests. “The presence of plutonium gives us a stark indicator of when humanity became such a dominant force that it could leave a unique global ‘fingerprint’ on our planet,” explained Professor Andrew Cundy, Chair in Environmental Radiochemistry at the University of Southampton and member of the Anthropocene Working Group. “In nature, plutonium is only present in trace amounts. But in the early-1950s, when the first hydrogen bomb tests took place, we see an unprecedented increase and then spike in the levels of plutonium in core samples from around the world. We then see a decline in plutonium from the mid-1960s onwards when the Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty came into effect.” Agreeing on a simple measure that defines the boundary between chapters in Earth’s history is just the first step. This measure requires agreement among scientists on a single location to define the boundaries. Known as the Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point, or a golden spike, plays a crucial role in standardising these borders between epochs. The Anthropocene Working Group has been evaluating potential golden spike sites, from Oued Akrech, Morocco, to Alano di Piave, Italy. After spending three years assessing the qualities of a dozen potential golden spikes for the Anthropocene, finally the AGW has landed on Crawford Lake. “Crawford Lake is so special because it allows us to see at annual resolution the changes in Earth history throughout two separate periods of human impact on this small lake,” micropalaeontologist Francine McCarthy of Brock University in Canada, a voting member of the AGW, said at a press briefing. The lake’s unique properties, such as its small size, depth, and lack of water mixing create sediments that precisely record environmental changes over the past millennia. To officially establish the Anthropocene in the International Chronostratigraphic Chart, the golden spike at Crawford Lake must undergo a series of voting by various commissions and unions. If successful, it will mark the moment when human activities permanently altered the planet. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-16 17:29
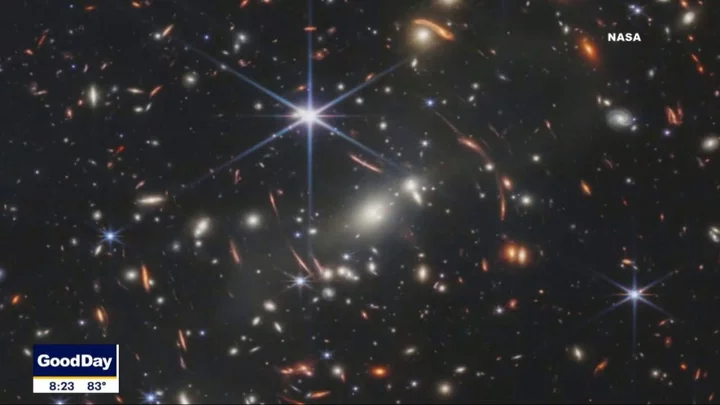

Nasa just uncovered mysterious new type of star ‘powered by dark matter’
A mysterious new set of stars has been detected by Nasa’s James Webb Space Telescope, which could shed new light on dark matter. Dark matter remains one of the most hotly debated elements in our solar system, and the new objects could change the way it is studied. Scientists believe the huge, newly-discovered stars are powered by illusive dark matter and shared their findings in the journal PNAS. “Discovering a new type of star is pretty interesting all by itself, but discovering it’s dark matter that’s powering this – that would be huge,” said study co-author Katherine Freese from The University of Texas in Austin. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The dark stars, known as JADES-GS-z13-0, JADES-GS-z12-0 and JADES-GS-z11-0 – were first identified as galaxies last December. It’s thought that they existed about 320-400 million years after the Big Bang, making them some of the earliest objects ever seen. The nature of dark matter continues to fascinate and mystify the scientific community. It’s believed that it could be formed by a new type of undiscovered particle, and the theorised component of the universe does not absorb, reflect or emit light. It’s also thought that suspected dark stars like these could explain a potential anomaly surrounding the number of large galaxies in the early universe. Currently, there are too many to fit the predictions of the theories surrounding the origins and the future of the universe. “It’s more likely that something within the standard model [of cosmology] needs tuning, because proposing something entirely new, as we did, is always less probable,” Dr Freese said. “But if some of these objects that look like early galaxies are actually dark stars, the simulations of galaxy formation agree better with observations,” she explained. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-15 19:18
