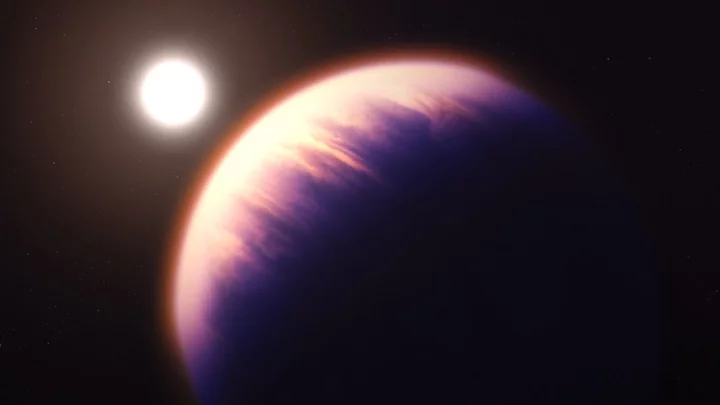

Scientists discover huge exoplanet 120 light years from Earth that ‘could contain signs of life’
An exoplanet more than eight times the size of Earth and potentially habitable has been discovered by scientists. Exoplanet K2-18 b was detected by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and piqued scientists’ interest after data suggested it may be covered in an ocean and have a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that could support life. Scientists are also encouraged by a hint of the detection of the molecule dimethyl sulphide (DMS). On Earth, DMS is only produced by microbial life, but the team has yet to confirm the detection and search for evidence of biological activity. The groundbreaking discovery of K2-18 b may see the exoplanet come under the unique classification of a “Hycean” planet – ones which are candidates for life thanks to their hydrogen-rich atmospheres and water cover. The amount of methane and carbon dioxide combined with the shortage of ammonia suggests there may be a water ocean underneath a hydrogen-rich atmosphere in K2-18 b. K2-18 b lies within the constellation of Leo and orbits a dwarf star called K2-18. It lies around 120 light years away from Earth and is within the habitable zone. However, scientists added that this does not necessarily mean it can support life. Nikku Madhusudhan, an astronomer at the University of Cambridge and lead author of the paper, explained: “Our findings underscore the importance of considering diverse habitable environments in the search for life elsewhere. “Traditionally, the search for life on exoplanets has focused primarily on smaller rocky planets, but the larger Hycean worlds are significantly more conducive to atmospheric observations.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-12 17:22
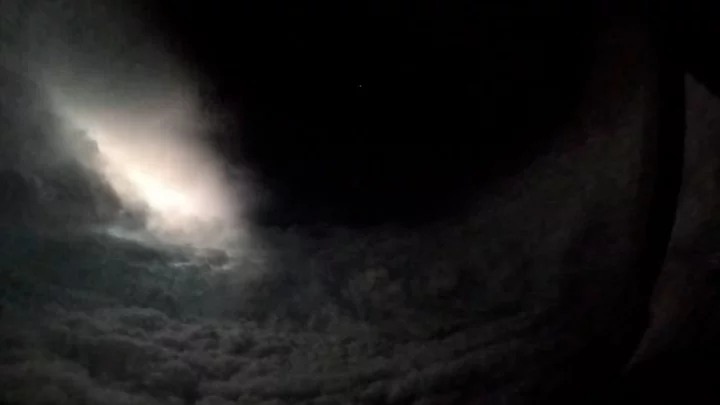

Storm chasers capture frightening footage from inside Hurricane Lee
Storm chasers filmed the inside of a hurricane and it looks just as terrifying as you might imagine it would. The footage taken from inside the eye of Hurricane Lee was captured on Friday (8 September) as the storm moved over the Atlantic Ocean. The video taken shows lightning striking inside the Category 4 hurricane, illuminating the cloud wall around it and with the black eye overhead. The stunning clip was captured by the U.S. Air Force Reserve's 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron in Biloxi, Mississippi. They are affectionately known as the “Hurricane Hunters”. As a Category 4 storm, Hurricane Lee has sustained winds of between 130 to 156 mph. The storm was located off the coast of Puerto Rico and was forecast to move northwards. The footage was able to be captured thanks to the squadron’s WC-130J Hercules aircraft. These planes are specifically designed for flying weather reconnaissance and have equipment onboard including sensors and instruments to measure the profile of a hurricane’s wind, temperature and pressure. The Hercules aircraft can stay airborne for up to 18 hours ensuring the crew onboard can record the weather data over a long time period. In a statement released by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) National Hurricane Center, they were unable to determine what the impact of the storm might be on the country’s eastern coast yet. The statement read: “It remains too soon to know what level of impacts, if any, Lee might have along the U.S. East Coast and Atlantic Canada late this week.” Hurricane Lee is the fourth hurricane to be recorded during the 2023 Atlantic hurricane season, along with nine other named storms. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-11 23:23
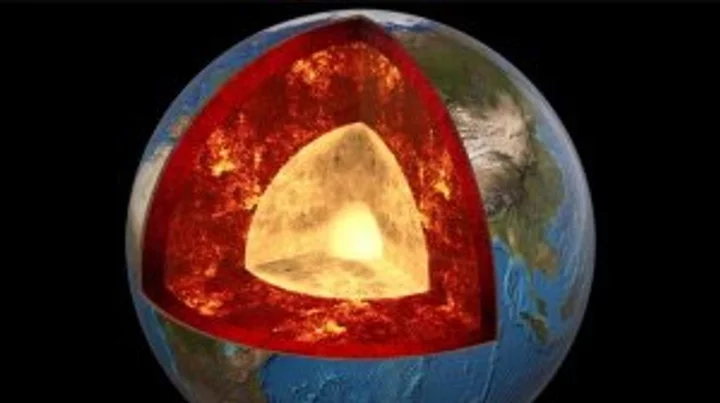
'Mountains' taller than Everest discovered on 'ancient structure' around Earth's core
A new study into the Earth beneath our feet has discovered that an ancient ocean floor structure could be wrapped around the planet's core which could be taller that Mount Everest in some areas. A brand new high-resolution mapping of the core has uncovered things that scientists previously didn't know according to a study that was first published in April. The discovery found that a thin but dense layer sits at around 2,900 kilometers below the surface at the Core Mantle Boundary where rocks meet the molten outer core of the planet. Geologist Samantha Hansen from the University of Alabama is quoted in the study saying: "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought." She adds: "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet.” Hansen and her team conducted the research from 15 different stations in Antarctica by using seismic waves created by Earthquakes to create a map of what the inside of the planet looks like. The team identified the unexpected energy within seconds of the boundary-reflected wave from the seismic data. The findings show that although the layer is very thin it does spread for many, many kilometers and has been called the ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZs) due to its strong wave speed reductions. Due to the properties of the ULVZs the experts believe that the layer could vary dramatically in height. Geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University adds: "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." These underground mountains could play a significant role in how heat escapes from the Earth's core and power magnetic fields and volcanic eruptions. The team's studies suggest that the layer could encase all of the core but further research will have to be carried out to determine if that is the case. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-10 19:26
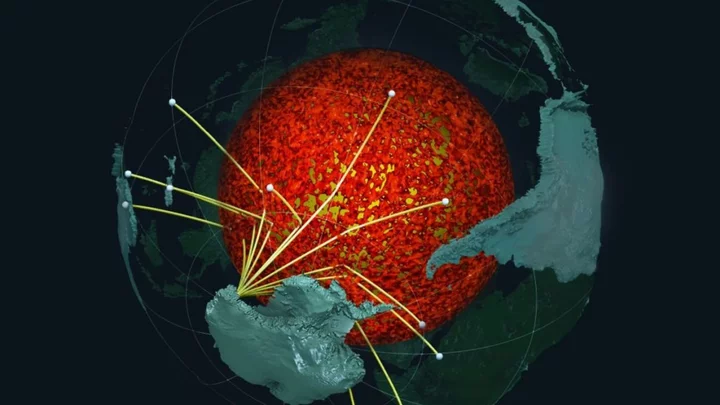
Underground 'mountains' discovered on Earth's core five-times taller than Mt. Everest
A new study into the Earth beneath our feet has discovered that an ancient ocean floor structure could be wrapped around the planet's core which could be taller that Mount Everest in some areas. A brand new high-resolution mapping of the core has uncovered things that scientists previously didn't know according to a study that was first published in April. The discovery found that a thin but dense layer sits at around 2,900 kilometers below the surface at the Core Mantle Boundary where rocks meet the molten outer core of the planet. Geologist Samantha Hansen from the University of Alabama is quoted in the study saying: "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought." She adds: "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet.” Hansen and her team conducted the research from 15 different stations in Antarctica by using seismic waves created by Earthquakes to create a map of what the inside of the planet looks like. The team identified the unexpected energy within seconds of the boundary-reflected wave from the seismic data. The findings show that although the layer is very thin it does spread for many, many kilometers and has been called the ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZs) due to its strong wave speed reductions. Due to the properties of the ULVZs the experts believe that the layer could vary dramatically in height. Geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University adds: "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." These underground mountains could play a significant role in how heat escapes from the Earth's core and power magnetic fields and volcanic eruptions. The team's studies suggest that the layer could encase all of the core but further research will have to be carried out to determine if that is the case. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-09 19:54
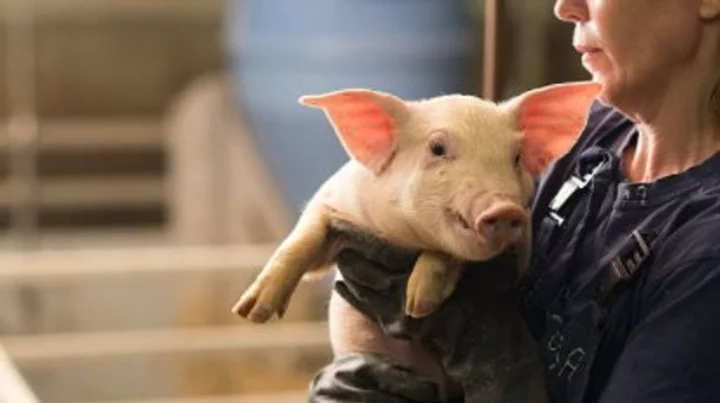

Scientists grow human kidneys inside a pig for the first time
Scientists have grown human kidneys in pigs, for the very first time. Researchers at the Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Wuyi University created human-pig chimeric embryos containing a combination of human and pig cells. When they transferred into 13 surrogate pig mothers, they developed kidneys that contained mostly human cells at a rate of 50 to 60 per cent, giving hope for potential transplants in the future. “Rat organs have been produced in mice, and mouse organs have been produced in rats, but previous attempts to grow human organs in pigs have not succeeded,” said the senior author Liangxue Lai. “Our approach improves the integration of human cells into recipient tissues and allows us to grow human organs in pigs.” The kidneys were not entirely human as they included vasculature and nerves made mostly from pig cells, meaning they could not be used for transplantation in their current form, but it is still a pretty impressive step. And apart from the kidneys, the embryos were dominated by pig cells, with very few human cells in the brain or central nervous system. Making brains using human and pig cells is very controversial for ethical reasons, so there are tight regulations for this kind of research. Meanwhile, pig cells tend to outcompete human cells during development, so previous experiments have created embryos that are almost entirely pig. The latest work, published in Cell Stem Cell, overcame this by genetically engineering a single-cell pig embryo so that it lacked two genes needed for kidney development. This created a gap within the embryo that could be filled by human cells. “We found that if you create a niche in the pig embryo, then the human cells naturally go into these spaces,” said Prof Zhen Dai of Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, another senior author. The scientists said that being able to incubate a fully human kidney inside a pig would be likely to take many years. “We would probably need to engineer the pigs in a much more complex way and that also brings some additional challenges,” said Miguel Esteban, also of the Guangzhou institute and a senior author. A central challenge would be to allow human nerves and vasculature to develop within the target organ without nerve cells developing in the central nervous system that could lead to a humanised brain. “Even theoretically it’s not clear how you’d do that,” said Ilic. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-08 19:49
Human embryo created without using sperm or eggs
Scientists in Israel have created a model of a human embryo from stem cells, without using sperm, eggs or a womb. A team at Israel's Weizmann Institute of Science made the model, which resembles an embryo at day 14, when it acquires internal structures but before it lays down the foundations for body organs, and the work was published in the journal Nature. But the scientists involved said it would take a long time yet to create an embryo from scratch. Team leader Jacob Hanna said the team took stem cells derived from adult human skin cells, as well as others cultured in the lab, then reverted the cells to an early state.They then manipulated them to make a model of an embryo, rather than an actual or synthetic one. "The question is, when does an embryo model become considered an embryo? When that happens, we know the regulations. At the moment we are really, really far off from that point," Hanna said. However, they said the work could open the door to new ways to test the effect of drugs on pregnancies, better understand miscarriages and genetic diseases, and maybe grow transplant tissues and organs. "They are not identical. There are differences from human embryos, but still, this is the first time, if you open an atlas or a textbook, you can say - yeah I can really see the similarity between them," said Hanna. "In about 1 percent of the aggregates we can see that the cells start differentiating correctly, migrating and sorting themselves into the correct structure, and the farthest we could get is day 14 in human embryo development," he said. Their next goal, Hanna said, is to advance to day 21 and also reach a threshold of a 50 per cent success rate. Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz, a professor of development and stem cells at the University of Cambridge, said the study joins six other similar human embryo-like models published from teams around the world this year, including from her lab. "None of these models fully recapitulate natural human development but each adds to ways in which many aspects of human development can now be studied experimentally," she said. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-08 18:26

Scientists confused after black holes 'burp up' previously destroyed stars
It feels like every time black holes are discussed and studied by the scientific community, there are new findings that blow our tiny minds. It’s been revealed that black holes actually regurgitate or “burp up” the stars that they eat years after the event. Experts made the discovery by studying tidal disruption events (TDEs). These events take place when stars are close enough to supermassive black holes, to be destroyed by the process of spaghettification. Studying these moments over a number of years after the black holes seemingly swallowing stars with no trace, the experts found that up to 50 per cent of them "burp up" the remains. Yvette Cendes is a research associate at the Havard and Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and head author on the study. Speaking to Live Science, she said: "If you look years later, a very, very large fraction of these black holes that don’t have radio emission at these early times will actually suddenly 'turn on' in radio waves. "I call it a 'burp' because we’re having some sort of delay where this material is not coming out of the accretion disk until much later than people were anticipating." The material was re-emitted between two and six years from 10 out of 24 black holes which were studied by Cendes and the team. It has the potential to change the way the scientific community thinks about black holes. "There was a second peak, the two black holes re-brightened, and that's completely new and unexpected," Cendes said. "People were thinking that you'd have one outflow, and then it's kind of done. So this observation means these black holes can 'turn on' and then 'turn on' again." Meanwhile, a low intergalactic grumbling is emanating from deep space, according to scientists – and again, it’s black holes that are providing us with new discoveries. Astronomers say they detected the first-of-their-kind low frequency ripples, described as a “cosmic bass note” of gravitational waves, which is thought to be caused by supermassive black holes merging across the universe. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-07 00:21

Frozen humans could be brought back to life in next 50 years claims expert
Experts may have found a way to resurrect frozen humans in 50 to 70 years. It comes after a cryonics company was able to revive an extinct worm from 46,000 years ago, leading them to believe the method could be applied to humans. "Cryonics is a scientifically based, legal technology for preserving humans and animals in a state of deep cooling in the hope that in the future they will be resuscitated and, if necessary, cured and rejuvenated," Russian cryogenics company KrioRus explained. "For legal reasons, human cryopreservation can be carried out only after legal death." KrioRus shared how the dead patient is "immersed into a low-temperature medium where almost all chemical reactions are stopped." The first ever cryopatient, American professor James Bedford, has been preserved for almost 50 years "with no sign of change or deterioration." "In the prognosis of modern science, a cryopatient can indeed be someday revived and return to life," they said. Many more people have opted to freeze their deceased pets, with costs dependent on pet size, species and distance to the facility among other factors. A dog is said to cost around $25,000. The company claims to have cryopreserved 92 people but disclaimed that for humans to be resurrected, there must be significant progress in the medical field. "Cryobiological laboratories are few, there are no large ones at all," CEO Valeriya Udalova told MailOnline. "Even the famous laboratory 'XXI Century Medicine' is a small organization." She continued: "But even in such a deplorable situation, remarkable experiments have already been made, for example, on reversible cryopreservation of a rat kidney using gas persufflation with nanoparticles and induction heating." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-06 21:15

Curly hair may have been critical to human evolution
Curly hair may have been absolutely critical to humans evolving millions of years ago, scientists have discovered. In fact, having curly hair could have been the key reason as to why humans developed, grew taller and came to have larger brains. It’s all to do with regulating body temperature, according to a new study by researchers at Penn State University. Given that hair can help to protect the head from the sun’s rays, it’s thought that thicker, curlier hair types could have been key to human life progressing in Equatorial Africa. Scientists recreated the kinds of conditions that early humans would have experienced, using wigs featuring different hair types on models. They found that curls were most effective in keeping the models cool in an environment measuring 86 degrees Fahrenheit (30 degrees Celsius) and 60 per cent humidity. Tina Lasisi is the study's lead author. She spoke to Newsweek about the findings and said: "We hypothesized that tightly curled scalp hair would provide some benefits, but the extent of these benefits was uncertain. "Previous studies on mammalian coats have shown that hair can limit the amount of sunlight reaching the skin, but we were particularly surprised by the significant reduction in solar heat radiation impact provided by tightly coiled hair.” The reduction in heat caused by tight curls could have led to the development of larger brains. "Once humans developed large brains, they could employ other behavioral and social strategies to cope with heat, potentially diminishing the relative advantage of curly hair," she said. "This could have led to a diverse distribution of hair textures worldwide. Furthermore, since straight hair better retains heat, populations in colder environments may have experienced selective pressure for straight hair." She added: "Future research should aim to answer these questions by incorporating our data into mathematical models of human physiology or conducting experiments with human subjects who have different hair textures to examine the impact on their thermal regulation.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-06 00:50

Mysterious 'golden egg' discovered at the bottom of the ocean leaves scientists baffled
A mysterious golden object has been found at the bottom of the ocean by scientists exploring the Pacific Ocean and it has left them baffled. The discovery was made on 30 August when a team of experts from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) were taking a closer look at an underwater volcano 250 miles off the coast of Alaska. Experts, and members of the public viewing the live stream, caught a glimpse of the unusual gold orb two miles beneath the surface lodged into the side of the volcano and were left puzzled over what it could be. It was found thanks to the NOAA’s Seascape Alaska 5 expedition that is currently mapping the seafloor of the Gulf of Alaska. Those who made the discovery at the foot of the volcano also noted there was a mysterious hole in the side of the orb, with one researcher suggesting on the live stream that “Something tried to get in...or to get out”. Scientists bantered back and forth about what the egg-like object could be and ultimately decided to take a sample that could be analysed. The texture of the orb was not as they had expected and was more of a silky, delicate consistency. An arm from the robotic vehicle was used to suction the orb in order for scientists to determine its origins with laboratory testing. The NOAA Seascape Alaska 5 expedition is due to end in mid-September and aims to fill the gaps that experts have about the sea beds off the USA’s west coast. It began on 24 August in Kodiak, Alaska and will come to an end in Seward, Alaska on 16 September. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-05 22:57

The Moon is slowly drifting away from Earth and its beginning to impact us
The Moon is a constant in the night sky, but all is not actually as it seems. It turns out that scientists have discovered the Moon is drifting away from Earth, and it’s changing everything we thought we knew about our planet’s relationship with its only natural satellite. It’s also having a very real impact on the length of days on our planet – albeit at an incredibly slow rate. By moving away from Earth over the course of millions of years, the Moon is simultaneously making the length of the average day longer. A study by a team at the University of Wisconsin-Madison focused on rock from a formation aged at 90 million years. By doing so, they were able to analyse the Earth’s interactions with the Moon 1.4 billion years ago. It turns out that the Moon is moving away from Earth at us at 3.82 centimetres a year. That means that, eventually, it’ll result in Earth days lasting 25 hours in 200 million years time. Stephen Meyers, who is a professor of geoscience at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, said: “As the moon moves away, the Earth is like a spinning figure skater who slows down as they stretch their arms out.” He added: “One of our ambitions was to use astrochronology to tell time in the most distant past, to develop very ancient geological time scales. “We want to be able to study rocks that are billions of years old in a way that is comparable to how we study modern geologic processes.” It’s not the only story that changes our understanding of the Moon recently. Scientists have also just uncovered billions of years’ worth of secrets buried beneath the surface of the moon – all thanks to China’s space programme, which has uncovered hidden structures which can help us start to piece together the Moon’s past. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-04 20:21
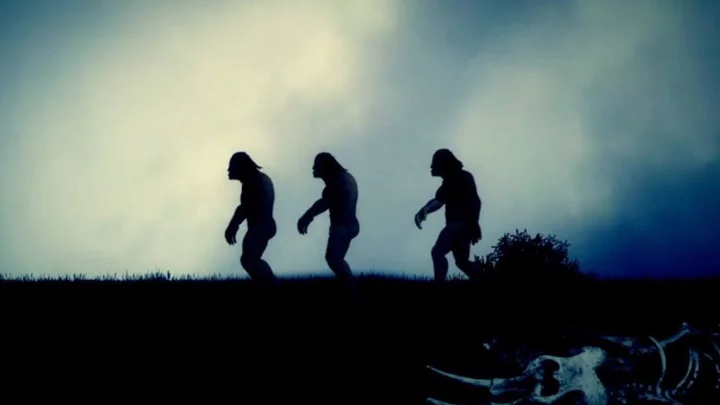

The terrifying time our early ancestors almost became extinct
New research has shown that our early ancestors almost went extinct some 900,000 years ago. Using a new method called FitCoal (fast infinitesimal time coalescent process), researchers analysed the likelihood of present-day genome sequences to project current human genomic variation backwards in time. They applied the technique to the genomes of 3,154 people from 10 African and 40 non-African populations, and found a massive crash in genetic diversity during the transition between the early and middle Pleistocene. “Results showed that human ancestors went through a severe population bottleneck with about 1,280 breeding individuals between around 930,000 and 813,000 years ago,” the study authors wrote in the journal Science. “The bottleneck lasted for about 117,000 years and brought human ancestors close to extinction,” they say. Wiping out roughly 98.7 percent of the ancestral human population, “the bottleneck could also have increased the inbreeding level of our ancestors, thus contributing to the 65.85 percent loss in present-day human genetic diversity,” explained the researchers. This probably happened because of changes in the global climate as short-term glaciations became longer-lasting, triggering a drop in ocean temperatures, prolonged drought, and the loss of large numbers of species that humans might have relied on for food. Then, around 813,000 years ago, populations finally recovered, with a 20-fold increase in numbers because of fire combined with the return of warmer temperatures, researchers reckon. What a near miss, eh? Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-03 19:55
