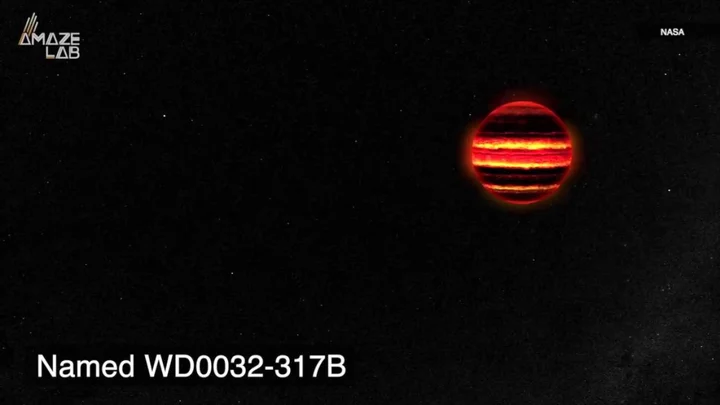

Astronomers have just discovered the most dazzling planet in the universe
Astronomers have just found out what planet in the universe is most dazzling and it is probably one you have never heard of. Looking at how much planet's clouds reflect sunlight back into space, astronomers have found a planet called exoplanet LTT9779b which reflects 80 per cent of the starlight it receives, making it the shiniest known planet in the universe. LTT9779b is slightly heavier and slightly larger than Neptune, and it is reflective because of the metallic glassy clouds that make up its atmosphere. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “Imagine a burning world, close to its star, with heavy clouds of metals floating aloft, raining down titanium droplets,” co-author James Jenkins, an astronomer at Diego Portales University and CATA (Santiago, Chile), said in a statement. Vivien Parmentier, a researcher at the Observatory of Côte d’Azur (France) and co-author of the study added: "LTT9779 b can form metallic clouds despite being so hot because the atmosphere is oversaturated with silicate and metal vapours.” So there you have it. Shame it doesn't have a very catchy name. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-11 18:55

Scientists capture the moment a black hole 'turns on'
Astronomers have spotted the moment a black hole "turned on". While looking for the collision of a neutron star with another object, which should result in a kilonova (an explosion which reddens then fades over time), they stumbled upon an event which remained extremely bright. They soon worked out this light was because of supermassive black hole called J221951-484240 which had been on for around 10 months. But then they had to work out what had caused it, and got stuck between two causes, “J221951 is consistent with being nuclear, so the scenarios we are being left are a tidal disruption event or an active galactic nucleus,” lead author Dr Samantha Oates said as she presented the research at the National Astronomy Meeting 2023. “Looking at the spectrum it's consistent with both categories.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter A tidal disruption event (TDE) takes place when a star or a gas cloud gets too close to a supermassive black hole. The material is ripped apart, and begins to shine as the black hole feeds Alternatively, it could be an active galactic nucleus (AGN), the phase of a supermassive black hole where it is consistently feeding in a frenzy. “We hope in future to distinguish between these two scenarios,” Dr Oates concluded. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-06 20:16
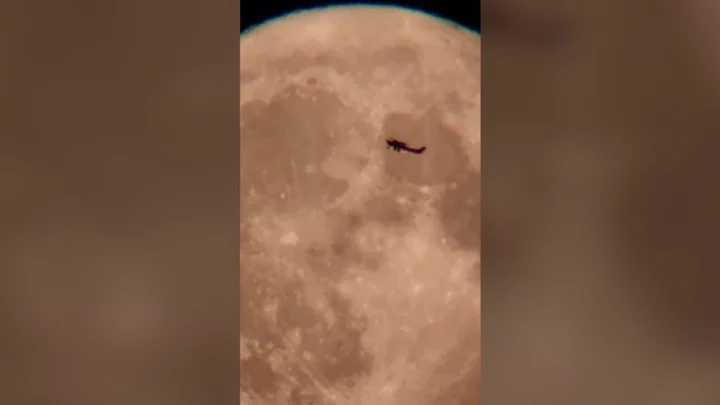

Supermoon completely dwarfs plane as it flies through Oregon skies in spectacular clip
July's Buck supermoon could be seen around the world lighting up the skies at the start of this week, but incredible new footage is showing the sheer scale of the phenomenon. A plane flying over the skies of Oregon is going viral after being filmed getting completely eclipsed by the moment. In the footage of the giant moon, the tiny plane goes flying past, and looks absolutely minuscule in comparison to the planet. Click here to sign up for our newsletters
2023-07-05 17:55
Scientists discover secret planet hiding in our solar system
There are eight planets in our solar system – plus poor old Pluto, which was demoted in 2006 – but what if there were more? Turns out that might be the case. Astronomers have calculated there is a 7 per cent chance that Earth has another neighbour hiding in the Oort cloud, a spherical region of ice chunks and rocks that is tens of thousands of times farther from the sun than we are. “It’s completely plausible for our solar system to have captured such an Oort cloud planet,” said Nathan Kaib, a co-author on the work and an astronomer at the Planetary Science Institute. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Hidden worlds like this are “a class of planets that should definitely exist but have received relatively little attention” until now, he said.. If a planet is hiding in the Oort cloud, it’s almost certainly an ice giant. Large planets like Jupiter and Saturn are generally born as twins. They have huge gravitational pulls of their own, however, and sometimes destabilise one another. That could have led to a planet to be nudged out of the solar system entirely – or exiled to its outer reaches, where the Oort cloud resides. “The survivor planets have eccentric orbits, which are like the scars from their violent pasts,” said lead author Sean Raymond, researcher at the University of Bordeaux’s Astrophysics Laboratory. That means that the Oort cloud planet could have a significantly elongated orbit, unlike the near-perfect circle Earth tracks around the sun. Trouble is, when things are that far away, they’re pretty difficult to spot. “It would be extremely hard to detect,” added Raymond. “If a Neptune-sized planet existed in our own Oort cloud, there’s a good chance that we wouldn’t have found it yet,” said Malena Rice, an astronomer at MIT not involved in this work. “Amazingly, it can sometimes be easier to spot planets hundreds of light-years away than those right in our own backyard.” Time to crack out the telescope. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-04 23:16
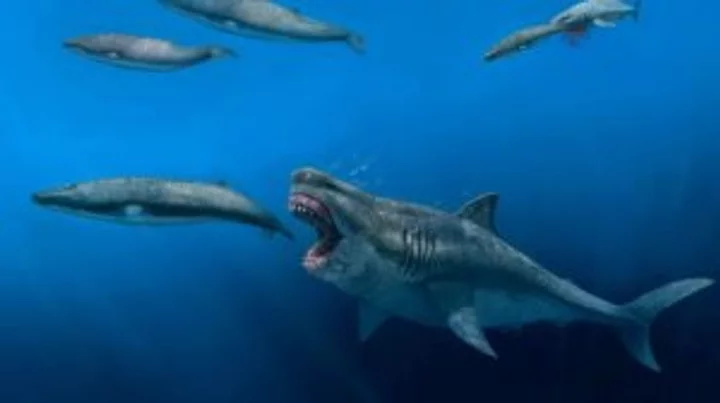

Scientists discover that megaladon's went extinct because of themselves
Scientists believe they have discovered the cause of the megalodon's extinction – and no, it’s not Jason Statham. Experts have been conducting research on fossils of teeth from the biggest species of shark the world has ever seen, which went extinct around 3.6 million years ago and measured at least 15 metres long. Research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences explains that the animal was actually partially warm-blooded. Unlike most cold-blood sharks, the body temperature is thought to have been around 27 degrees. The temperature is higher than the sea temperatures around the time. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Study co author Robert Eagle, who is professor of marine science and geobiology at UCLA, said [via CNN]: “We found that O. megalodon had body temperatures significantly elevated compared to other sharks, consistent with it having a degree of internal heat production as modern warm-blooded (endothermic) animals do.” They were able to prove that the animals were warm-blooded by analysing how carbon-13 and oxygen-18 isotopes were closely bonded together in the fossilised teeth. Senior study author Kenshu Shimada is a paleobiologist at DePaul University in Chicago, who said: “A large body promotes efficiency in prey capture with wider spatial coverage, but it requires a lot of energy to maintain. “We know that Megalodon had gigantic cutting teeth used for feeding on marine mammals, such as cetaceans and pinnipeds, based on the fossil record. The new study is consistent with the idea that the evolution of warm-bloodedness was a gateway for the gigantism in Megalodon to keep up with the high metabolic demand.” The fact it was warm-blooded means that regulating body temperature could have been the cause of its eventual demise. The Earth was cooling when the animal went extinct, which could have been a critical factor. “The fact that Megalodon disappeared suggests the likely vulnerability of being warm-blooded because warm-bloodedness requires constant food intake to sustain high metabolism,” Shimada said. “Possibly, there was a shift in the marine ecosystem due to the climatic cooling,” causing the sea level to drop, altering the habitats of the populations of the types of food megalodon fed on such as marine mammals and leading to its extinction. “One of the big implications for this work is that it highlights the vulnerability of large apex predators, such the modern great white shark, to climate change given similarities in their biology with megalodon,” said lead study author Michael Griffiths, professor of environmental science, geochemist and paleoclimatologist at William Paterson University. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-04 21:49
Scientists discover secret planet hidden in our solar system
There are eight planets in our solar system – plus poor old Pluto, which was demoted in 2006 – but what if there were more? Turns out that might be the case. Astronomers have calculated there is a 7 per cent chance that Earth has another neighbour hiding in the Oort cloud, a spherical region of ice chunks and rocks that is tens of thousands of times farther from the sun than we are. “It’s completely plausible for our solar system to have captured such an Oort cloud planet,” said Nathan Kaib, a co-author on the work and an astronomer at the Planetary Science Institute. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Hidden worlds like this are “a class of planets that should definitely exist but have received relatively little attention” until now, he said.. If a planet is hiding in the Oort cloud, it’s almost certainly an ice giant. Large planets like Jupiter and Saturn are generally born as twins. They have huge gravitational pulls of their own, however, and sometimes destabilise one another. That could have led to a planet to be nudged out of the solar system entirely – or exiled to its outer reaches, where the Oort cloud resides. “The survivor planets have eccentric orbits, which are like the scars from their violent pasts,” said lead author Sean Raymond, researcher at the University of Bordeaux’s Astrophysics Laboratory. That means that the Oort cloud planet could have a significantly elongated orbit, unlike the near-perfect circle Earth tracks around the sun. Trouble is, when things are that far away, they’re pretty difficult to spot. “It would be extremely hard to detect,” added Raymond. “If a Neptune-sized planet existed in our own Oort cloud, there’s a good chance that we wouldn’t have found it yet,” said Malena Rice, an astronomer at MIT not involved in this work. “Amazingly, it can sometimes be easier to spot planets hundreds of light-years away than those right in our own backyard.” Time to crack out the telescope. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-30 15:26

'Alien spacecraft' found at the bottom of Pacific Ocean
For years people have been looking to the skies for signs of alien life - but maybe, they should have been looking at the bottom of the ocean this whole time. A Harvard physicist has claimed that parts of an alien 'spacecraft' could have been uncovered under the sea. Professor Avi Loeb set off on a search along the bottom of the Pacific Ocean and found 50 iron pieces which originated from the IM1 meteor. IM1 crashed off the coast of Papua New Guinea and Leob believes it could contain key information in the search for life out there in the universe, saying he hasn’t discounted the idea of the pieces being evidence of a “spacecraft” from an “extraterrestrial technological civilization” which crashlanded on Earth. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Loeb is currently the head of Harvard’s Galileo Project, focusing on the search for aliens, and he said the fragments they found must have come from “a natural environment different from the solar system, or an extraterrestrial technological civilization.” Speaking to Fox News Digital, Loeb detailed his thoughts on the origins of the meteor fragments by saying: “Given IM1's high speed and anomalous material strength, its source must have been a natural environment different from the solar system, or an extraterrestrial technological civilization.” He added that IM1 “is actually tougher and has material strength that is higher than all the space rocks that were catalogued by NASA. That makes it quite unusual.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-29 21:27
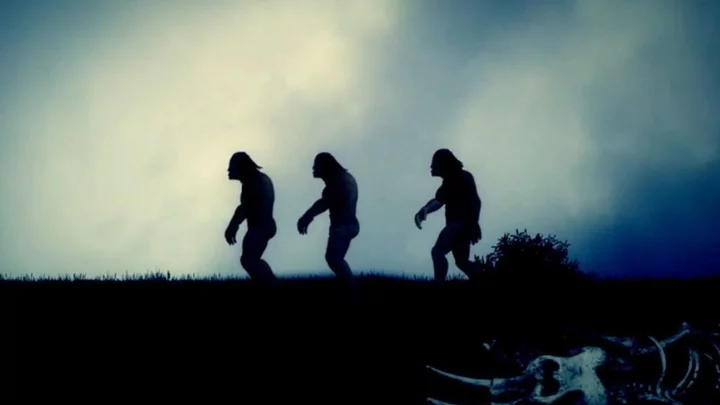

Everybody alive today came from one African country, according to study
It’s well known that all humans alive today can be traced back to a common ancestor but a study may have found where that ancestor originates. Researchers at the University of Oxford’s Big Data Institute mapped the entirety of genetic relationships among humans to create the largest human family tree ever. By combining modern and ancient human genomes data from eight different databases, the researchers were able to create a massive family tree. This allowed them to see how a person’s genetic sequence relates to another using the points of the genome. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “Essentially, we are reconstructing the genomes of our ancestors and using them to form a vast network of relationships,” Lead author Dr Anthony Wilder Wohns said. “We can then estimate when and where these ancestors lived.” Where they lived? Sudan, Africa. Dr Wohns told Reuters, "The very earliest ancestors we identify trace back in time to a geographic location that is in modern Sudan. “These ancestors lived up to and over 1 million years ago—which is much older than current estimates for the age of Homo sapiens—250,000 to 300,000 years ago. So bits of our genome have been inherited from individuals who we wouldn’t recognize as modern humans," Dr Wohns said. Researchers used 3,609 individual genome sequences from 215 populations and samples that ranged from 1,000s to over 100,000 years. By using a new method to compile the data, algorithms were able to predict where common ancestors were in evolutionary trees to explain some patterns of genetic variation. The results were a network of almost 27 million ancestors. “The power of our approach is that it makes very few assumptions about the underlying data and can also include both modern and ancient DNA samples,” Dr Wohns says. Not only does the data help us understand human geology better but the new method could help in other research, like medicine. “The underlying method could have widespread applications in medical research, for instance identifying genetic predictors of disease risk," Dr Wohns added. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-29 18:21
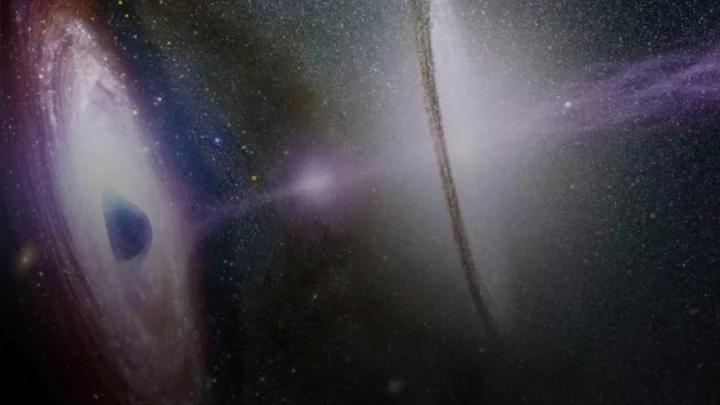

Stephen Hawking theory proved right by man-made black hole
Scientists have managed to simulate their very own black hole in their lab and witnessed how it began to glow. The black hole event horizon was created by a team of physicists from the University of Amsterdam, who used a chain of atoms in a single file to gain further understanding about the behaviour of a black hole. Its creation managed to prove Stephen Hawking's theory from 1974 where the black hole emitted a rare form of radiation. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter They studied the properties of Hawking radiation through the creation of a black hole analog in the lab. According to Science Alert, Hawking radiation happens when "particles born from disturbances in the quantum fluctuations caused by the black hole's break in spacetime." The fact that the radiation exhibits a glow itself is in a strange space anomaly, as the event horizon of a black hole is supposed to be where neither light nor matter is able to get out. We all learn about the strength of a black hole in science class – and how we would all be inevitably sucked in as a result. This is possible due to its density within a certain range of the centre, so even an attempt at travelling beyond light speed (or any velocity in the universe for the matter) would not make this unavoidable. The fake black hole event also caused a rise in temperature that matched theoretical expectations of an equivalent black hole system, - but only when part of the chain extended beyond the event horizon, Science Alert reported. As a result, it is believed perhaps this entanglement of particles that straddle the event horizon plays a big role in generating Hawking radiation. Under simulations that began by mimicking spacetime thought of as "flat," scientists say the radiation was only thermal for a certain range of 'hop amplitudes'. So there may be certain situations where Hawking radiation can emit thermally - and could only be the case where gravity causes a change in the warp of space-time. "This can open a venue for exploring fundamental quantum-mechanical aspects alongside gravity and curved spacetimes in various condensed matter settings," the scientists wrote in their paper published by Physical Review Research. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-06-29 18:19

Scientists discover gigantic 'structure' under the surface of the Moon
The Moon has been a subject of awe and fascination for millennia, with its shape-shifting powers and enigmatic dark side. And though it’s the one celestial body on which man has taken (small) steps, we still have big leaps to go in understanding its potential and uncovering its secrets. However, one hidden feature of the Moon has been unearthed by scientists and it’s very, very big, and very, very heavy. Buried beneath its South Pole-Aitken basin – one of the largest preserved craters in the Solar System – is a structure which weighs at least 2.18 billion kilogrammes and measures more than 300km (186 miles) in depth and 2,000km (1,243 miles) in length. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The researchers who made the discovery, all based in the US, posited that the “anomaly” could be made out of metal from the core of an asteroid or oxides from the crystallisation of a magma ocean. "One of the explanations of this extra mass is that the metal from the asteroid that formed this crater is still embedded in the Moon's mantle,” lead author Peter B. James, from Houston’s Baylor University, said in a statement shared with IFLScience. Illustrating just how gigantic this thing is, he went on: "Imagine taking a pile of metal five times larger than the Big Island of Hawaii and burying it underground. That's roughly how much unexpected mass we detected.” The groundbreaking finding was made thanks to NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, which measures changes in the Moon’s gravitational field. Data collected by GRAIL can then be used to study the internal composition of our cratered companion. The South Pole-Aitken Basin has been at the centre of numerous investigations because of just how unique it is. The region offers clues both on the interior composition of our closest satellite and its history, and who knows what other mysteries it holds... Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-29 17:54
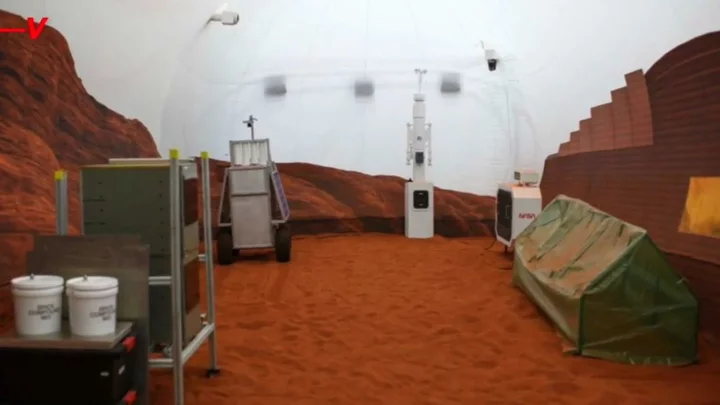

Four Nasa volunteers are living on 'virtual Mars' for the next 12 months
Would you sign up to live in isolation for a year, all in the name of furthering scientific research? Probably not, we’re guessing, but that’s exactly what four NASA volunteers have agreed to do over the next 12 months. The participants will live in an environment created to simulate conditions on the surface of Mars as part of NASA's Crew Health and Performance Exploration Analog for 378 days. The people involved are research scientist Kelly Haston, structural engineer Ross Brockwell, emergency medicine physician Nathan Jones and US Navy microbiologist Anca Selariu. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The simulation has been built at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, and will see the four volunteers undertake a series of tasks as part of the exercise. Data collected over the next 12 months will help to inform future missions to send astronauts to Mars. During that time, the guests will take part in activities such as crop growing as well as simulated spacewalks and other operations. The 3D-printed hub they’ll spend their time in contains a kitchen, sleeping areas, two bathrooms as well as work and recreation spaces. The mission will also see the guests faced with simulated obstacles, which are designed to test responses to equipment failure, communication delays and other issues. Speaking at a recent briefing, the mission's principal investigator at NASA Grace Douglas said: “Thank you all for your dedication to exploration. Our best wishes go with you." Haston also spoke, calling her fellow participants an "amazing group of dedicated individuals who feel very passionate about space exploration and science." "The crew has worked so hard this month to get ready for this mission," Haston added. "It has been very special to be a part of such a tremendous group of scientists and specialists from a diverse set of backgrounds working together to bring CHAPEA 1, the first of three missions, to reality." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-28 21:54

Astronomers discover a totally new way that stars can die
Astronomers have discovered a new way that stars can die. In a study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, experts have worked out that a minute-long gamma-ray burst of light, which occured in 2019 and evidence a star dying, happened because stars collided within the densely crowded environment near the supermassive black hole at the centre of an ancient galaxy. Normally gamma-ray bursts (GRB) last around two seconds and happen when stars collapse. “For every hundred events that fit into the traditional classification scheme of gamma-ray bursts, there is at least one oddball that throws us for a loop,” said study coauthor Wen-fai Fong, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern University’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, in a statement. “However, it is these oddballs that tell us the most about the spectacular diversity of explosions that the universe is capable of.” Over time, astronomers have observed three main ways that stars can die, depending on their size. Lower mass stars like our sun shed their outer layers as they age, eventually becoming dead white dwarf stars. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Massive stars burn through the fuel-like elements at their core and shatter in explosions called supernovas. Doing so can leave behind dense remnants like neutron stars or result in the creation of black holes. A third form of star death results when neutron stars or black holes begin to orbit one another in a binary system and spiral closer to one another until they collide and explode. But the new observation suggests a fourth type of death. “Our results show that stars can meet their demise in some of the densest regions of the universe, where they can be driven to collide,” said lead study author Andrew Levan, an astrophysics professor at Radboud University in Nijmegen, Netherlands, in a statement. “This is exciting for understanding how stars die and for answering other questions, such as what unexpected sources might create gravitational waves that we could detect on Earth.” “The lack of a supernova accompanying the long GRB 191019A tells us that this burst is not a typical massive star collapse,” said study coauthor Jillian Rastinejad, a doctoral student of astronomy at Northwestern, in a statement. “The location of GRB 191019A, embedded in the nucleus of the host galaxy, teases a predicted but not yet evidenced theory for how gravitational-wave emitting sources might form.” “While this event is the first of its kind to be discovered, it’s possible there are more out there that are hidden by the large amounts of dust close to their galaxies,” said Fong, who is also a member of the Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics at Northwestern. “Indeed, if this long-duration event came from merging compact objects, it contributes to the growing population of GRBs that defies our traditional classifications.” You learn something new every day. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-26 19:27
