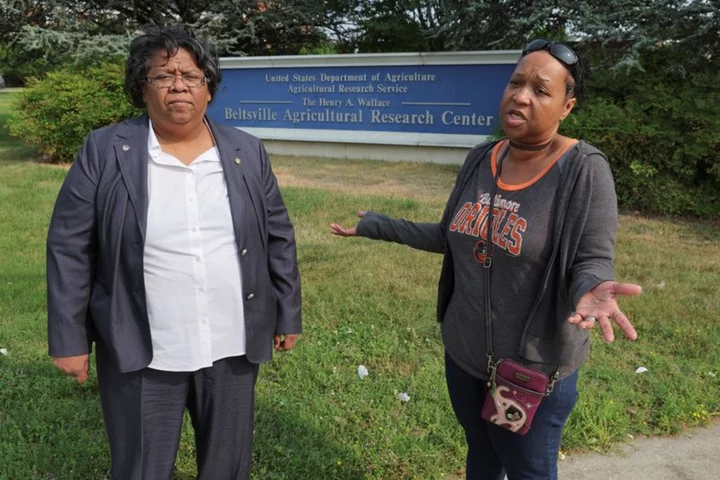

Exclusive-Staff at top U.S. farm research center file complaint alleging unsafe work conditions
By Leah Douglas Three employees of the largest agricultural research facility in the U.S. have filed federal whistleblower
2023-05-19 19:17
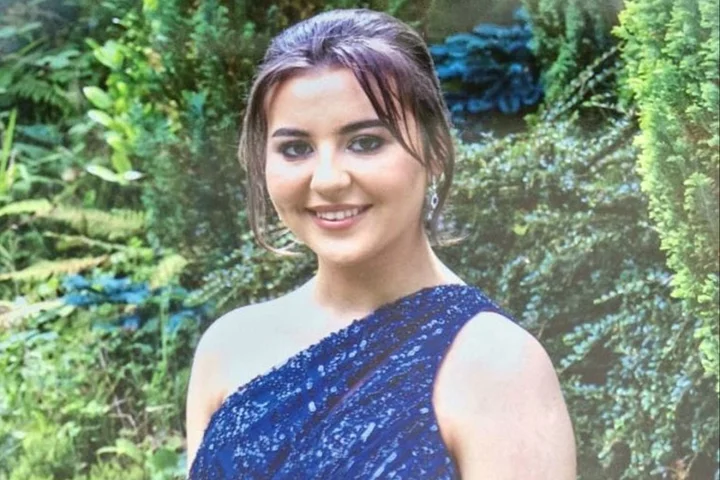

Boyfriend of teenager killed with three friends in car crash reveals tragic moment he found out
The boyfriend of a teenager killed along with three others in a car crash on the way to celebrate exam results has revealed the tragic way he found out. Aaron Costin had been in a relationship with Grace McSweeney for two years and received a message from the 18-year-old on Snapchat just before she got into the car. Minutes after seeing her location on the app, Aaron’s friend sent him a text saying there had been a crash on the road Grace was on. Grace’s brother Luke McSweeney, 24, along with Zoey Coffey, 18, and Nicole Murphy, 18, died at the scene in Clonmel, Co Tipperary, after the car they were travelling in struck a wall. Mr McSweeney was driving the teenagers to a bus on Friday when the car overturned and crashed into a wall. Aaron rushed to the scene but couldn’t get to the area because it was blocked off by police, he told The Sunday Times. “There was something in me that didn’t want to believe it was their car but I could see the car and then I knew what it was. It was hard,” he said. “She was bubbly, she was friendly. She was there for anyone, whenever you wanted. Her family made the home very welcoming.” Aaron had last seen Grace the day before the crash after she’d texted him worried about her results. He picked her up and they walked around Carey’s Castle, a short drive from Clonmel. The young couple met at a party organised by Zoey Coffey, 18, who also lost her life in the crash. Aaron said Grace and Zoey were inseparable, and the day he met Grace was the happiest day of his life. “She was one of the greatest women I’ve ever met in my life,” he added. The pair had been looking forward to a trip together to Amsterdam, which they had planned in part because of Grace’s love for history. She’d wanted to visit the Anne Frank House. Laying flowers at the scene on Sunday, Aaron said: “She was the love of my life.” The funeral for siblings Grace and Luke will take place on Friday and a book of condolences will open at County Hall in Clonmel on Monday. Parish priest Fr John Treacy said the funeral for Mr and Ms McSweeney would take place at St Peter and Paul’s Church in Clonmel at 11.30am on Friday. Father Treacy said “very difficult” days lay ahead for the families. “The love of a parent for their child, it’s an unspeakable and inseparable bond of love and fidelity, and tenderness and compassion, and to lose that is just something that words cannot adequately describe,” he told RTE Radio One. Aaron’s mother, Jennifer Costin, posted a tribute to Grace on Facebook the day after the crash. She wrote: “None of it seems real today. Thank you for making my son happy and I’ll do my best to mind him for you.” Around 2,000 people gathered in Clonmel for a vigil to mourn the death of the four youngsters on Sunday evening, with the location of the crash now adorned with flowers, notes and candles. Grieving family members and classmates of the victims of Friday evening’s crash were among those who attended the emotional event at Kickham Plaza. Classmates from Presentation Secondary School wore lilac jumpers that commemorate their graduate class of 2023. Speaking after Sunday’s vigil, Bishop of Waterford Alphonsus Cullinan said there was a “strength” in the community coming together in grief. “Because there’s so many people here, it just shows the strength of community that’s here, the bond that’s here,” he said. “Everyone here has a connection with what those three families and those four youngsters, God love them all. “So, there’s a real strength in that consoling one another, helping one another, to go through the grief, praying together, as well as singing together, crying together. “It’s heartbreaking and there’s no easy solution. There’s no easy words. We just have to find the strength to struggle on.” Gardai have launched an investigation to determine the cause of the crash, and are appealing for witnesses. Their investigation is currently focusing on preparing a report for the local coroner. Adverse weather conditions at the time of the crash, including heavy downpours at the scene when first responders arrived, will be considered as part of the inquiry. Read More Hundreds gather for Clonmel vigil to four young victims of horror car crash Support for Clonmel students will be in place for as long as needed – minister Leaving Cert students had received ‘excellent’ exam results hours before fatal crash Crafty Aussie makes button versions of music stars including Sir Elton John Explorer excited to add hydrogen balloon attempt to his Atlantic crossings Pittsburgh Steelers connect with Gaelic games to grow fan base in Ireland
2023-08-28 20:56

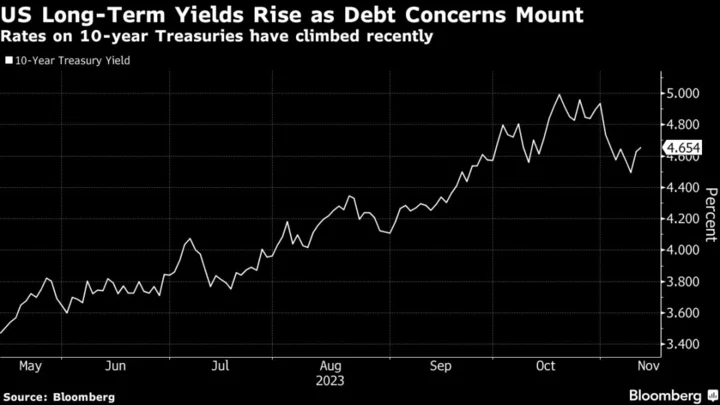
Threat of US credit downgrade looms over debt ceiling talks
With one of three major rating agencies warning that America’s AAA credit is at risk, the stakes are growing in the standoff in Washington over raising the nation’s debt limit
2023-05-26 00:26

University of Idaho murders: Moscow house where four students were killed to be demolished in 'a healing step'
The off-campus King Road residence will be torn down, and all personal belongings of the victims and their unharmed housemates will be removed
2023-06-30 16:57

The Fed wants to cool spending; a strike, a shutdown and student loans may add ice
By Howard Schneider WASHINGTON U.S. Federal Reserve officials, who have tentatively embraced the possibility they can squelch inflation
2023-09-19 10:28

Who was Patrice Wilson? Detroit nurse's family sues hospital for $200M over her kidnapping and murder by ex
Patrice Wilson's family is pursuing a $200M lawsuit against the hospital, claiming that they did not protect and ensure her safety during her shift
2023-08-02 20:21
Asia Stocks to Climb After Wall Street Tech Rally: Markets Wrap
Equity markets across Asia were primed to advance following a tech-driven rally Friday on Wall Street, as investors
2023-11-13 07:29

US consumer confidence ebbs in September
WASHINGTON U.S. consumer confidence fell for a second straight month in September amid worries about higher prices and
2023-09-26 22:23

Armenia says Pashinyan-Aliyev talks cancelled after Baku pulled out-TASS
MOSCOW (Reuters) -Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan's meeting with Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev, originally scheduled for late October in Brussels,
2023-10-25 19:21
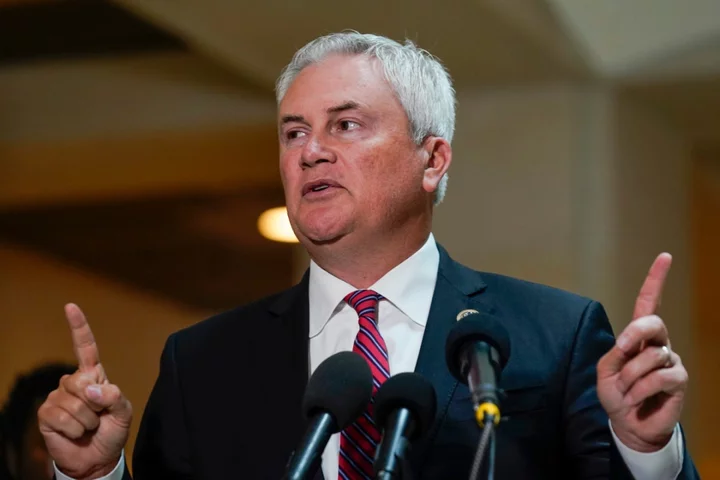

GOP cries foul over spy charges for Biden ‘whistleblower’
Four days after he claimed a “very credible witness” had emerged to provide the Justice Department with derogatory information about President Joe Biden and his family, House Oversight Committee chair James Comer questioned the timing of charges that the alleged whistleblower was actually spying for the Chinese government and attempting to broker illegal arms sales to Libya. The alleged unregistered foreign agent, Gal Luft, was arrested in February by authorities in Cyprus on arms trafficking charges, but he subsequently disappeared after jumping bail. Mr Luft, who is a citizen of both the United States and Israel, is accused of paying a former adviser to Donald Trump on behalf of principals in China in 2016 without registering as a foreign agent. Prosecutors say that Mr Luft pushed the former government employee, who is not named, to push policies that were favourable to China, and further accuse him of having set up meetings between officials of Iran and a Chinese energy company to discuss oil deals, which would violate US sanctions. Mr Comer, who appeared on Fox News late Monday, insinuated that the charges against the think tank founder were meant to silence him when asked about the timing by host Laura Ingraham. “The timing is always coincidental, according to the Democrats at the Department of Justice,” he said. The Kentucky Republican claimed that Mr Luft was being paid by the same company which entered into a failed business venture with Mr Biden’s son, Hunter Biden, and suggested that the speed at which the department moved against Mr Luft is suspicious. “So there are a lot of questions here and it's just amazing. The Department of Justice moves so quickly against some people,” he said, adding that it is ironic that Mr Luft is charged with being an unregistered foreign agent — the same allegation Republicans have levelled against Hunter Biden. The indictment announced on Monday also alleges that Mr Luft “conspired with others and attempted to broker illicit arms transactions with, among others, certain Chinese individuals and entities” by working as a middleman to find both buyers and sellers for “certain weapons and other materials” in violation of the US Arms Control Act. Specifically, prosecutors say he attempted to broker a sale of anti-tank weapons, grenade launchers and mortar rounds to Libya by Chinese companies, and also pushed to arrange for the United Arab Emirates to purchase bombs and rockets, and for Kenya to acquire unmanned aerial vehicles capable of striking targets on the ground. They further alleged that Mr Luft lied to FBI agents during an interview in 2019, when he claims to have provided the bureau with derogatory information on the Biden family. Asked whether the charges that Mr Luft made false statements to FBI agents in any way impacts his credibility as an alleged whistleblower against the president or his son, Mr Comer replied: “Did he lie to the FBI? I don’t know!” He also accused FBI leadership of lying to him “three times this year”. “I have no confidence in the FBI,” he said, adding that his lack of confidence in the country’s premier law enforcement agency was “sad”. One of his Republican colleagues on the House Oversight Committee, South Carolina Nancy Mace, also downplayed the charges in a TV appearance in which she accused the Biden administration of using the prosecution to stop Mr Luft from speaking out. Speaking on Fox Business Network on Tuesday, Ms Mace said Mr Luft “deserves to testify before the Oversight Committee” and accused the department of trying to keep him from doing so. “No one should be surprised here. I don’t trust the DOJ or the FBI, they are trying to silence our witness and this is a way to do that,” she said. She added that it is “obscene” that the government is not charging Hunter Biden with the same crimes despite the fact that Mr Biden has never attempted to broker arms sales or violate US sanctions on Iran. Read More ‘Whistleblower’ who accused Bidens of corruption is charged with arms trafficking and violating Iran sanctions Marjorie Taylor Greene introduces amendment directing Biden to withdraw from Nato Joint Chiefs nominee wins over lawmakers but faces uncertain fate because of senator's hold Biden blames busy schedule for skipping Nato leadership dinner
2023-07-12 07:18

Lab crunch: British science has nowhere to go
By Kate Holton OXFORD, England For Ros Deegan, the thrill of raising $100 million to expand a biotech
2023-06-20 14:53

Start your week smart: Debt ceiling deal, Texas impeachment, Russian drone attack
CNN's 5 Things brings you the news you need to Start Your Week Smart.
2023-05-28 21:21
You Might Like...

Who is Prospero Serna? California man arrested for the death of two of his children found with lacerations on their bodies
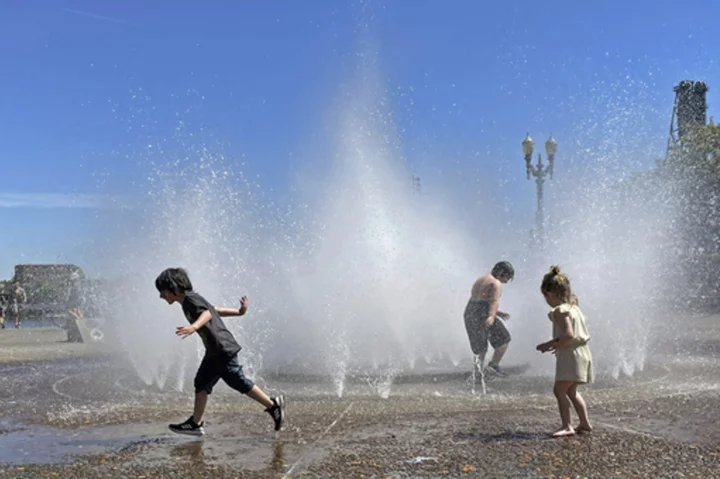

Unusually early heat wave in Pacific Northwest could break records
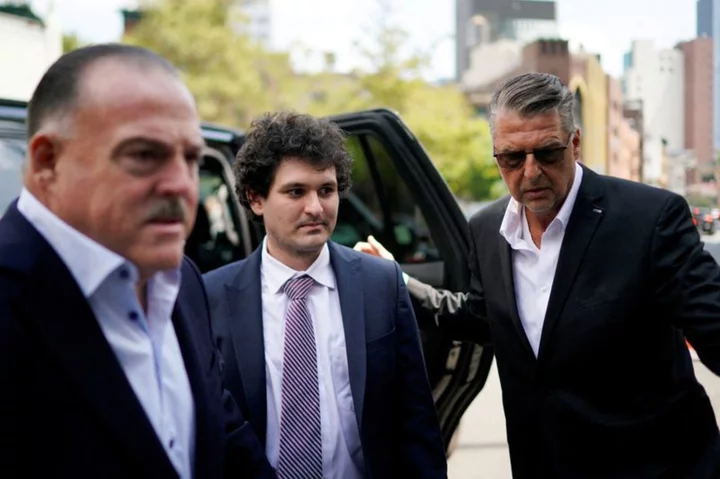

Sam Bankman-Fried's ex-girlfriend set to take stand as fraud trial's star witness
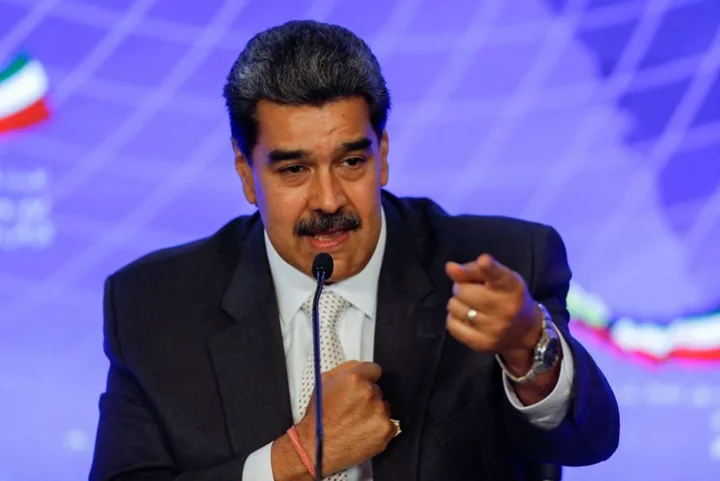

US broadly eases Venezuela oil sanctions after election deal

'Jeopardy!' host Ken Jennings slammed by former contestant Wil Wheaton for hosting amid WGA strike, calls him 'a scab'
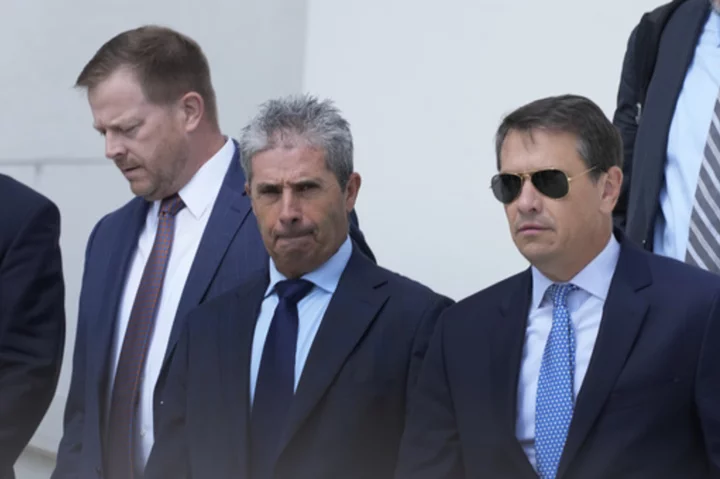

Mar-a-Lago property manager pleads not guilty to charges in Trump's classified documents case
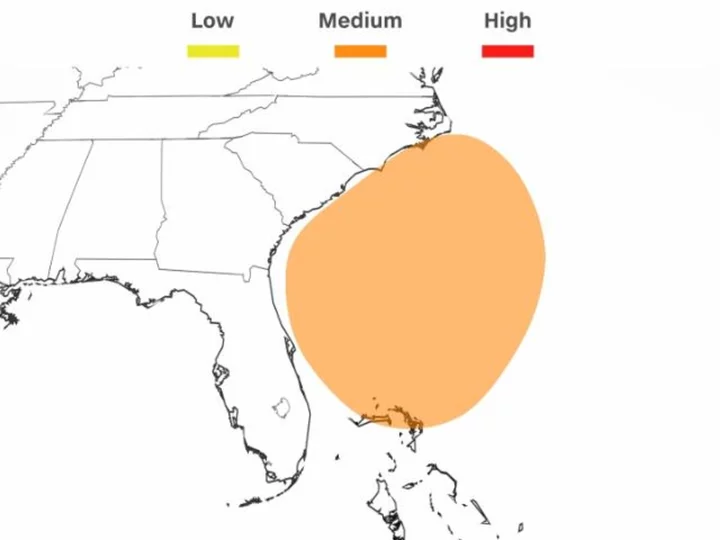
Tropical storm conditions possible for mid-Atlantic from coastal storm

Europe's Euclid space telescope set for launch to explore 'dark universe'
