
Reusable bottles contain 'more bacteria than toilet seats'
Reusable water bottles tick many boxes. Not only do they help you stay hydrated and help save money, but they also help cut down on single-use plastic. They've almost become a fashion accessory, with chic stainless steel flasks and viral bottles going viral across TikTok. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Trying to hit the NHS-recommended eight glasses of water a day for adults is an excellent idea, of course, but did you know there’s one way your refillable bottle could potentially be detrimental to your health? According to a study from waterfilterguru.com, reusable water bottles contain an average of 20.8m colony-forming units (CFUs) of bacteria, which equates to 40,000 times more than the microbes on a toilet seat. So what might be the consequences if you continuously sip and refill without washing your bottle properly between uses? We asked health experts to talk through the risks… Bottling up bacteria “A common misconception when it comes to reusable water bottle hygiene is that as you’re typically filling it with pure water and it’s only coming into contact with your own mouth, there’s little need to clean it often,” says Dr Donald Grant, senior clinician at The Independent Pharmacy. However, every time you drink from the bottle, you’re transferring bacteria from your mouth, which can then multiply in the container. “Anything that is reusable can be prone to accumulating dirt, dust or debris and, as a result, bacteria,” says private GP Dr Suhail Hussain. “This is exacerbated by the fact water bottles are the ideal environment for harbouring bacteria due to being moist.” Hard-to-reach crevices – for example, inside a screw top or under a flip-up straw – could also develop mould, and then there’s contamination from other sources. “When you store it in a gym bag, for instance, it can pick up bacteria from the interior of the bag or anything else stored in it, while you can also transfer bacteria from your hands to your bottle,” says Grant. “If your bottle has a valve cap, you may need to lift or twist it with your fingers, and this can transfer bacteria you may have picked up from touching other objects or surfaces.” What types of microbes are found in water bottles? “These might be simple commensals such as streptococcus and staphylococcus, which normally live in symbiosis with their host (i.e. us) but can become problematic if they accumulate or the individual is under the weather,” Hussain says. “Bacteria such as E. coli – a common cause of urine and bowel infections – can often colonise the water bottle following repeated handling, such as taking the cap on and off.” These bacteria can potentially cause a variety of issues. “You may become sick and develop gastric illness, such as diarrhoea or vomiting,” Hussain continues. “Gram negative rods – another common bacterium found in unwashed bottles – can lead to urogenital tract infections and pneumonia.” Grant warns: “If there’s a build-up of mould inside the bottle, this can cause allergy symptoms, such as a runny nose, sneezing, or red and itchy eyes. Symptoms might be more severe for someone with asthma.” How often should you wash your reusable water bottle? “To minimise your risk of getting sick, you should ideally clean your water bottle after each use,” Grant says. “As a minimum, you should aim to wash it thoroughly at least a few times a week.” Hot water and washing up liquid are all you need to banish bacteria on a daily. “Fill the bottle with hot soapy mixture and swill around, or leave to soak in a detergent mixture,” Hussain advises. “Remember to pay special attention to lids/caps and screw top regions – use a clean brush [to scrub them].” If you’ve neglected your bottle for a few days and it needs a deeper clean, Grant suggests: “Soak your bottle overnight in a solution of half vinegar and half water. Rinse the bottle and let it dry fully before using it again.” Storage is also important to help minimise nasty microbes. “Where possible, you should keep your water bottle out of germ-rich environments such as your gym locker or sports bag,” Grant says. “You should also avoid filling your bottle with anything other than water, such as protein shakes, energy drinks, or sugar-rich liquids, as sugar can stimulate the growth of bacteria.” Hussain adds: “Don’t leave a water bottle in the sun for long periods or sitting in the cup holder in the car – the mixture of warmth and moisture is likely to make bacterial overgrowth worse.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-24 17:21

How Do Fireworks Get Their Colors?
The chemistry behind the vibrant colors of fireworks is another reason to “ooh” and “aah” at the sky this Fourth of July.
2023-06-23 05:25

Scientists just created a new state of matter – here's what that means
Scientists have just created an entirely new state of matter made out of subatomic particles. The bosonic correlated insulator, to be precise, is both a new material and a new state of matter, said researchers from California, Arizona and Japan. There are four fundamental states of matter, liquid, solid, gas and plasma – an electrically charged gas found in situations like stars and lightning strikes. But there are many others when you drill down to quantum level (that means at an atomic and subatomic level). The scientists said this is a new one. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The new material is a lattice-shaped pattern, formed from a layer of the two different types of subatomic particles: bosons and fermions. Bosons are a type of particle which is difficult for scientists to create and manipulate because they do not interact with each other. Fermions are more stable – particles such as electrons – and interact through electrostatic force. The material sees the two different types of particle combining and interacting in a new way, with the particles eventually form into a crystalline state, which in turn creates a material which has an insulating effect. “Conventionally, people have spent most of their efforts to understand what happens when you put many fermions together,” says condensed matter physicist Chenhao Jin from the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB). “The main thrust of our work is that we basically made a new material out of interacting bosons.” The new material doesn’t yet have any practical uses, but exotic creations like this help scientists understand how the universe is put together, the team said. “What happened here is that we discovered the correlation that drove the bosons into a highly ordered state,” said physicist Richen Xiong, from UCSB. The scientists think the discovery could lead to them finding more materials like this further down the line. “We know that some materials have very bizarre properties,” said Xiong. “And one goal of condensed matter physics is to understand why they have these rich properties and find ways to make these behaviours come out more reliably.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-22 18:16
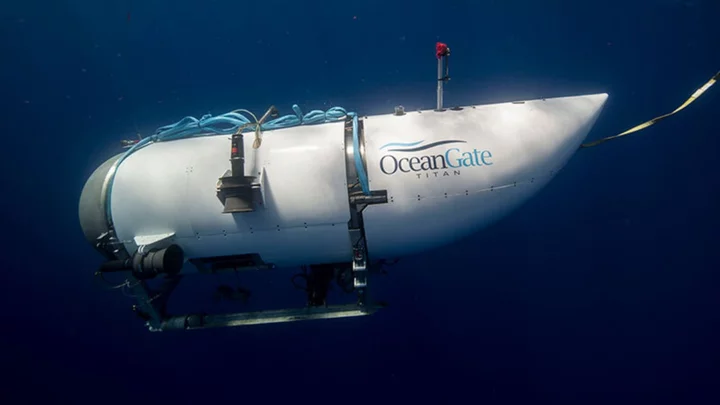

Submarine vs. Submersible: What’s the Difference?
There’s a reason nobody’s referring to the missing ‘Titanic’ submersible as a submarine.
2023-06-22 02:49
Titanic Vessel Search Detects Signs of Life, Explorers Club Says
An international exploration club with members on board the submersible missing near the Titanic wreck suggested “likely signs
2023-06-21 12:51

If you have blue eyes you may have a higher risk of alcoholism
Research from the University of Vermont suggests that there may be a link between those who have blue eyes and alcoholism. The study, conducted in 2015, was led by Dr Arvis Sulovari and assistant professor Dawei Li, and was the first to draw a direct connection between the colour of someone's eyes and their risk of developing alcoholism. Professor Li generated a database comprising of more than 10,000 individuals who have received a diagnosis for at least one psychiatric illness, including conditions such as addiction. Speaking of the conditions, Li - an expert in microbiology and molecular genetics - explained that they were "complex disorders" and that "many genes" and "environmental triggers" were involved. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The researchers used the database to identify those with a dependency on alcohol and discovered an interesting correlation. They found that those with lighter colour eyes - especially blue - had greater rates of alcohol addiction. The researchers even checked three times to be sure of their findings. "This suggests an intriguing possibility that eye colour can be useful in the clinic for alcohol dependence diagnosis," said Dr Sulovari. The study also found that the genetic components that determine eye colour and those associated with excessive alcohol use share the same chromosome. However, more tests and studies are going to have to take place in order for us to gain a deeper understanding of the potential link between eye colour and higher rates of alcohol dependency. Researchers are still unsure as to why there is such a link. With professor Li saying that much of genetics is "still unknown". Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-20 23:20

United States media guide
An overview of the media in the United States, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-06-20 17:17

Scientists found the oldest water on the planet and drank it
If you found water that was more than two billion years old, would your first instinct be to drink it? One scientist did exactly that after finding the oldest water ever discovered on the planet. A team from the University of Toronto, led by Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar, came across an incredible find while studying a Canadian mine in 2016. Tests showed that the water source they unearthed was between 1.5 billion and 2.64 billion years old. Given that it was completely isolated, it marked the oldest ever found on Earth. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Remarkably, the tests also uncovered that there was once life present in the water. Speaking to BBC News, professor Sherwood Lollar said: “When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock. “But in fact it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of litres per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.” Discussing the presence of life in the water, Sherwood Lollar added: “By looking at the sulphate in the water, we were able to see a fingerprint that’s indicative of the presence of life. And we were able to indicate that the signal we are seeing in the fluids has to have been produced by microbiology - and most importantly has to have been produced over a very long time scale. “The microbes that produced this signature couldn’t have done it overnight. This has to be an indication that organisms have been present in these fluids on a geological timescale.” The professor also revealed that she tried the water for herself – but how did it taste? “If you’re a geologist who works with rocks, you’ve probably licked a lot of rocks,” Sherwood Lollar told CNN. She revealed that the water was "very salty and bitter" and "much saltier than seawater." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-20 14:55

Lab crunch: British science has nowhere to go
By Kate Holton OXFORD, England For Ros Deegan, the thrill of raising $100 million to expand a biotech
2023-06-20 14:53

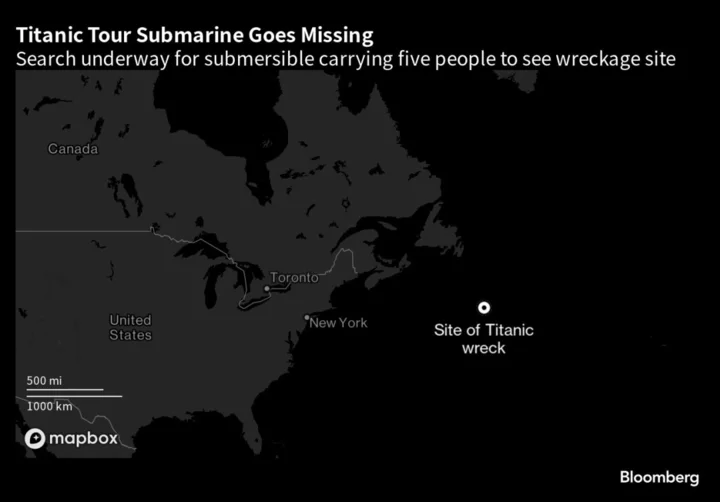
Search Underway for Titanic-Wreck Submersible With Five Crew
Searchers raced to find a submersible diving vessel with five people aboard that went missing in the North
2023-06-20 14:30

A scientists found the oldest water on the planet and drank it
If you found water that was more than two billion years old, would your first instinct be to drink it? One scientist did exactly that after finding the oldest water ever discovered on the planet. A team from the University of Toronto, led by Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar, came across an incredible find while studying a Canadian mine in 2016. Tests showed that the water source they unearthed was between 1.5 billion and 2.64 billion years old. Given that it was completely isolated, it marked the oldest ever found on Earth. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Remarkably, the tests also uncovered that there was once life present in the water. Speaking to BBC News, professor Sherwood Lollar said: “When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock. “But in fact it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of litres per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.” Discussing the presence of life in the water, Sherwood Lollar added: “By looking at the sulphate in the water, we were able to see a fingerprint that’s indicative of the presence of life. And we were able to indicate that the signal we are seeing in the fluids has to have been produced by microbiology - and most importantly has to have been produced over a very long time scale. “The microbes that produced this signature couldn’t have done it overnight. This has to be an indication that organisms have been present in these fluids on a geological timescale.” The professor also revealed that she tried the water for herself – but how did it taste? “If you’re a geologist who works with rocks, you’ve probably licked a lot of rocks,” Sherwood Lollar told CNN. She revealed that the water was "very salty and bitter" and "much saltier than seawater." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-19 22:57

Scientists create human embryo with a heartbeat without using sperm or eggs
Scientists have created a model human embryo to study the first weeks of life, complete with a heartbeat and traces of blood. The synthetic embryo was created with human stem cells and did not require sperm, eggs or fertilisation. It mimics the structure that occurs during the first month of pregnancy. Yet, scientists ensured it was designed to not form a foetus. Researchers involved in the extraordinary project discovered that the model had early stages of developing a brain and beating heart cells, which generally develop after 23 days in a human embryo. It was achieved through embryonic stem cells, which are 'blank' cells from a human embryo. Scientists grew the model in a lab before transferring it to a rotating bottle to act as an artificial uterus, The Guardian reported. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Scientists hope the findings will help them understand more about the impact of genetic disorders and miscarriage. Dr Jitesh Neupane, of the University of Cambridge’s Gurdon Institute, told the publication: "I randomly took my plate under the microscope and when I saw the [heartbeat] for the first time I was scared, honestly. I had to look down and look back again. "It was overwhelming for me. People get emotional when you see the heartbeat." He went on to emphasise that the model is "neither embryos nor are [they] trying to make embryos actually." "They are just models that could be used to look into specific aspects of human development," he continued. The findings are yet to be published in either a preprint or a journal paper. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-19 17:22
