
‘Busted’: Internet blasts ‘RHONJ’ star Joe Gorga as he assures reimbursement for fake show tickets, claims he got 'scammed'
Joe Gorga claimed that he got scammed and promised to provide people reimbursement for comedy show tickets
2023-11-01 11:57
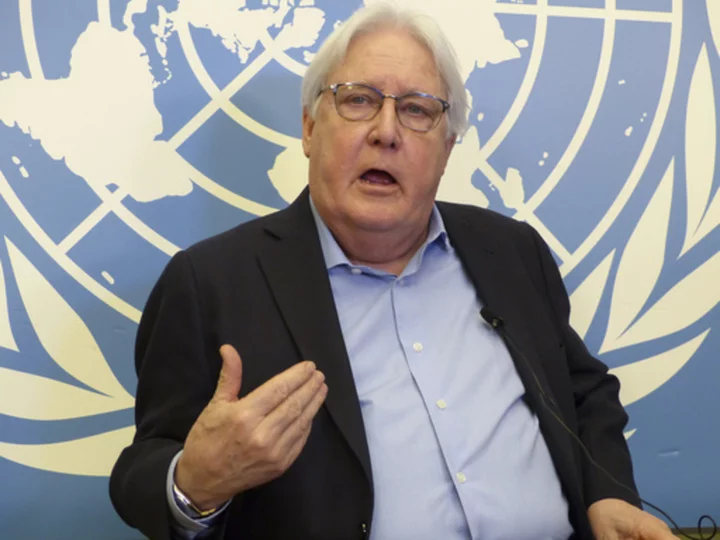

UN official hopes for breakthrough on Russian food, fertilizer shipments
A top U.N. official says he hopes for a breakthrough soon after months of efforts to ensure that Russian food and fertilizer can be shipped to developing countries struggling with high prices
2023-05-19 01:59
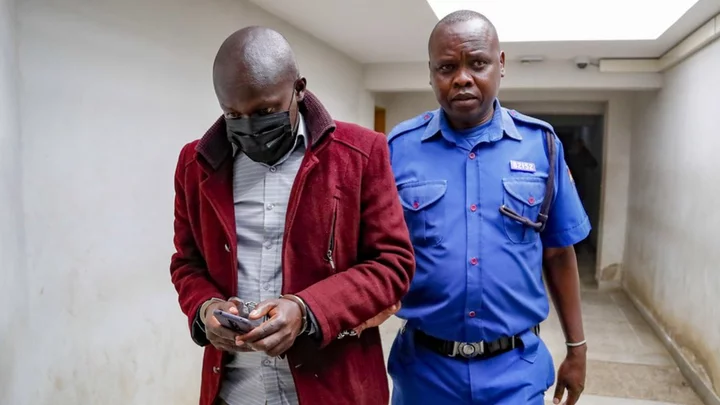

Kenyan baby stealer convicted after BBC expose
Hospital worker Fred Leparan attempted to sell a baby boy to an undercover BBC reporter.
2023-09-06 21:21

How did Elizabeth Hoffman die? Actress known for playing the role of mother of 4 siblings on 'Sisters' was 97
Elizabeth Hoffman died of natural causes at her home in Malibu, California, on August 21, her family said in a statement
2023-10-24 06:15

The View's Ana Navarro labeled 'pathetic' for calling Joe Biden 'unconditionally loving dad': 'You aren't a serious person'
‘The View’ is currently on hiatus, but it seems Ana Navarro is making sure the viewers of the chat show have plenty of content to talk about
2023-07-09 11:15

Sudan fighting intensifies despite US sanctions
Shelling rocked greater Khartoum on Friday, as fighting between Sudan's warring generals intensified despite US sanctions imposed after the collapse of...
2023-06-02 22:17

When was Josey Dorsey born? Naya Rivera's ex-husband and son keep 'Glee' star's memories 'alive' after her death
Naya Rivera died in 2020 after accidentally drowning during a boating trip with her son
2023-07-09 20:26
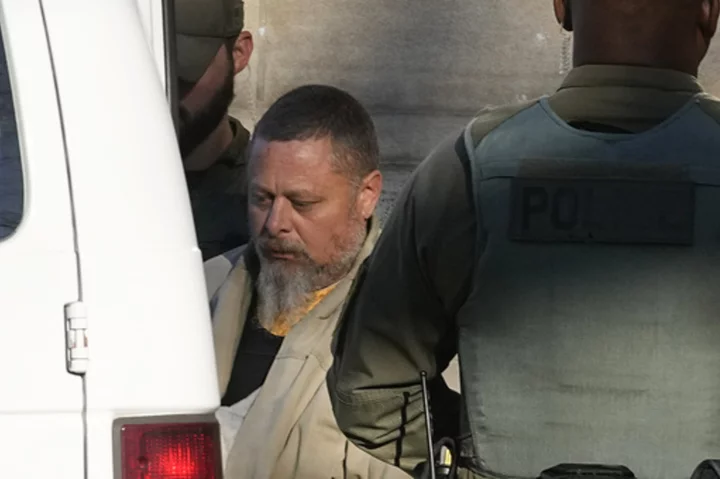

Attorneys for an Indiana man charged in 2 killings leave case amid questions of evidence security
An Indiana judge says two attorneys representing a man accused in the 2017 slayings of two teenage girls are withdrawing from the case unexpectedly
2023-10-20 05:47

US prices stay high, showing inflation pressures persist
Consumer prices in the United States rose again in April, and measures of underlying inflation stayed high, suggesting that rising costs could persist for months to come
2023-05-10 20:54
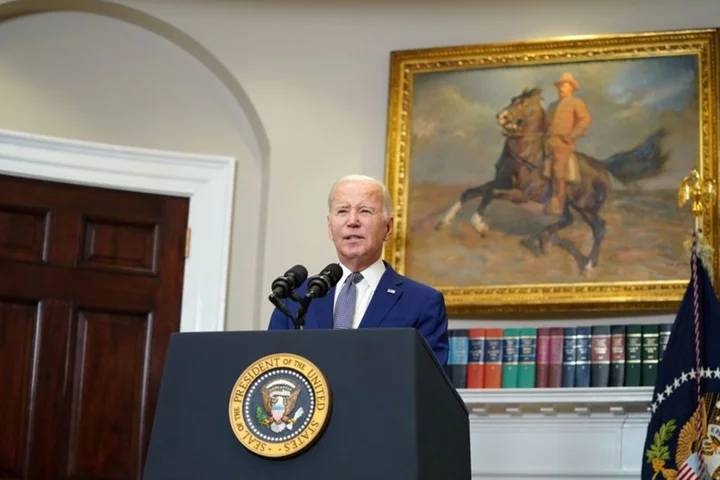

Biden speaks with US allies about Ukraine support, White House says
WASHINGTON U.S. President Joe Biden spoke with the leaders of allied countries, the European Union and the NATO
2023-10-03 23:28

Banning TikTok vs. protecting Twitter
Americans' commitment to freedom of speech is colliding with their dislike of the Chinese government and their addiction to social media.
2023-05-19 05:24
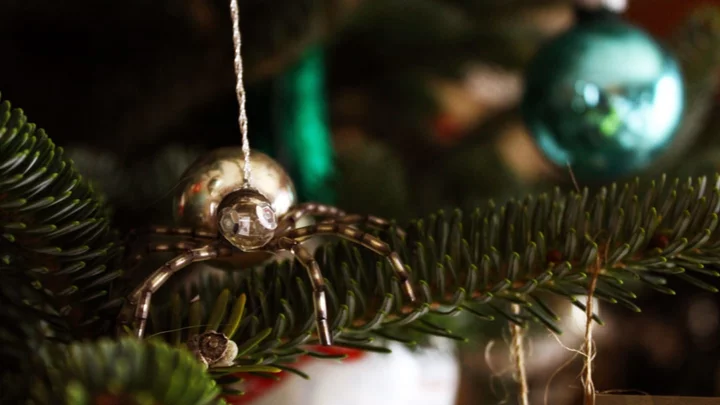

Why Ukrainians Hang Spider Webs on Their Christmas Trees
The Eastern European tradition is rooted in a beloved folktale often known as 'The Legend of the Christmas Spider.'
2023-11-11 00:26
You Might Like...
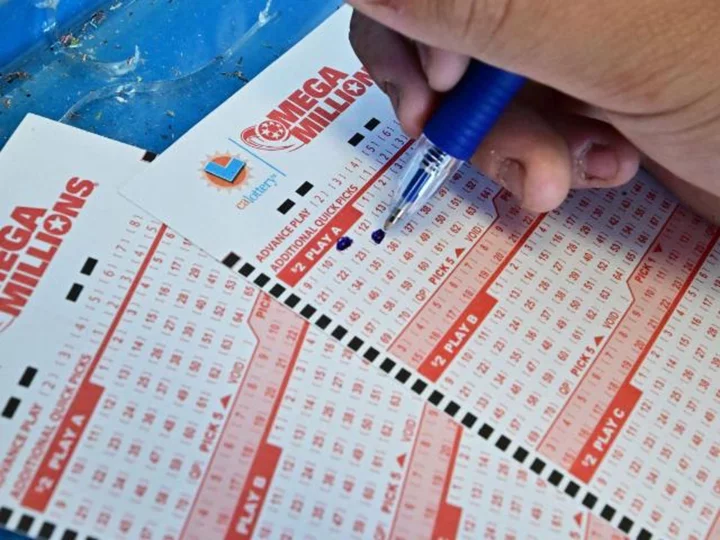

Tuesday night's $1.55 billion Mega Millions drawing could bring largest jackpot in the lottery's history

Top EU lawmaker says firewall against German far right stands, but willing to work with Meloni

Straight outta 'Jaws'! Multiple shark attacks leave waters bloody on 4th of July

Adin Ross invites fans to embrace his $150K legacy through streaming competition, followers wonder 'is this actually real?'
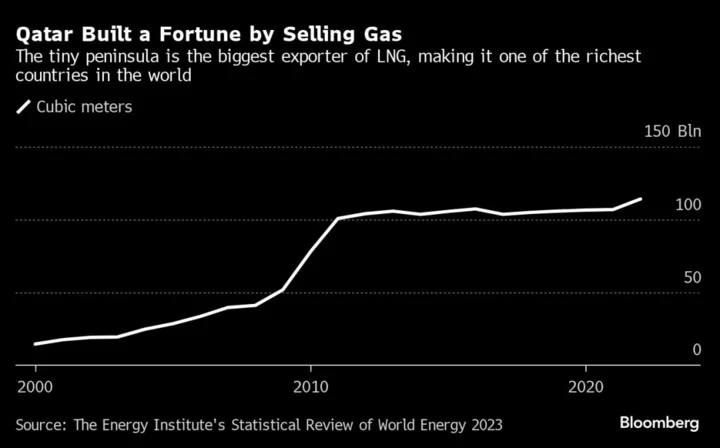
Israel-Hamas War Escalation Puts Qatar’s Clout to the Test

Kathy Kleiner Rubin: Here's why Ted Bundy survivor refused to attend his execution

Family of 11-year-old Mississippi boy shot by police files federal lawsuit seeking $5 million

California governor signs law requiring gender-neutral bathrooms in schools by 2026
