
What is 'trace evidence'? Investigators tight-lipped about findings inside home of alleged serial killer Rex Heuermann
Suffolk County District Attorney Raymond Tierney faced intense questioning regarding what was found in the basement of the family residence.
2023-07-26 18:25

10-year yields hit 16-year peak as Fed seen higher for longer
By Karen Brettell NEW YORK Benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury yields rose to 16-year highs on Thursday, a day
2023-09-21 22:24

Voice referendum: Australia to hold historic Indigenous vote in October
Voters will consider whether to recognise Indigenous people in the country's constitution.
2023-08-30 10:20

US soccer star Megan Rapinoe announces she’ll retire after the NWSL season
Megan Rapinoe has announced she’ll retire at the end of the National Women’s Soccer League season
2023-07-09 01:47

49ers trade quarterback Trey Lance to Cowboys, AP source says
The San Francisco 49ers have traded quarterback Trey Lance to the Dallas Cowboys less than three years after trading three first-round picks to draft him
2023-08-26 07:46

US decides to rejoin UNESCO and pay back dues, to counter Chinese influence
U.N. cultural and scientific agency UNESCO has announced that the United States plans to rejoin — and pay more than $600 million in back dues — after a decade-long dispute sparked by the organization’s move to include Palestine as a member
2023-06-12 19:27
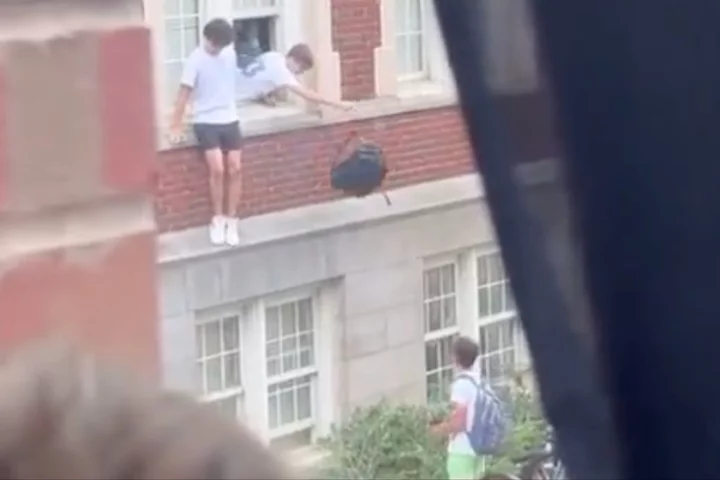

UNC students seen jumping from windows in heartwrenching videos during active shooter situation
Heartwrenching videos show students hiding under desks and jumping from classroom windows during an active shooter situation the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. The campus was placed on lockdown for several hours on Monday afternoon after an alert went out about an “armed person”. Police later confirmed one member of the faculty was killed and a suspect, identified as graduate student Tailei Qi, was taken into custody. The motive for the shooting, which took place at the centre of the campus in one of the science buildings, remains unclear. Throughout much of the active situation, those under the “shelter in place” order did not have any idea what was going on. Videos posted to social media captured sirens wailing as students and faculty barricaded themselves in dorms, bathrooms, classrooms, and gyms across the sprawling grounds. The shelter in place alert was posted just after 1pm, with sirens emitted within two minutes. Officers found the faculty member, who has not been identified, fatally shot in the lab building, UNC Police Chief Brian James told a press conference. The suspect was apprehended about 90 minutes after the initial report of gunfire but the lockdown persisted as authorities searched for the weapon, officials told a press at a briefing. The arrest took place in a residential area close to the campus, according to local TV station WRAL. The lockdown was lifted at about 4.15pm. It is unclear if the suspect and victim knew each other. Chief James said: “To actually have the suspect in custody gives us an opportunity to figure out the why and even the how, and also helps us to uncover a motive and really just why this happened today. Why today, why at all?” “And we want to learn from this incident and we will certainly work to do our best to ensure that this never happens again on the UNC campus,” he added. Chancellor Kevin Guskiewicz said: “This loss is devastating, and the shooting damages the trust and safety that we so often take for granted in our campus community.” Graduate student Clayton Ulm, 23, said he was in a class with about 50 to 70 others when the lockdown went into action. The alarm went off and screens in the room also announced the order to shelter in place. “Then there was quite a bit of panic as students were trying to figure out what to do,” Mr Ulm wrote on LinkedIn after three hours of the lockdown, according to the AP. “Then we all started hiding beneath our chairs and under desks. Some students went and locked the doors.” Mr Ulm added that students began listening to police scanners to find out where the shooter was located with the sense of panic eventually subsiding and students could use the restrooms near them. It was “surreal seeing the mass panic,” Mr Ulm said. “We are looking for a firearm. It is too early to determine if the firearm was legally obtained,” Chief James said. The shooting came just a week after the start of classes at the first public university in the US. Tuesday’s classes were cancelled for the school’s 20,000 undergraduates and 12,000 graduate students. Northern Virginia freshman Rushil Umaretiya held a candle outside the lab building on Monday night with two of his friends, just two weeks after he moved to Chapel Hill. “In my family, whenever someone passes, we light a candle, so I thought I’d come out and pay some respect to the community I’m trying to join,” he told the AP. “It’s a scary time for a lot of people, like I have a lot of history with loss, so I think it’s just fear and a lot of mixed emotions.” Mr Ulm moved from Oklahoma to Chapel Hill a couple of months ago. He told the news agency that his mother called him as the students were sheltering in place. She was “crying profusely,” he said. “I knew I should’ve texted you yesterday, I was so worried... this was my greatest fear,” she told him. Read More UNC Chapel Hill graduate student Tailei Qi charged with murder in shooting of faculty member UNC shooting – latest: Graduate student charged with murder of faculty member on Chapel Hill campus
2023-08-29 22:59
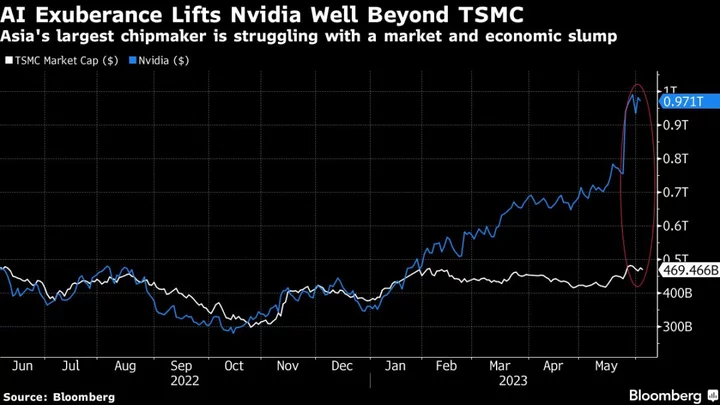
TSMC Tempers Capex Outlook to $32 Billion as Chip Demand Weakens
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. tempered its outlook for 2023 capital spending, as the main chipmaker to Apple Inc.
2023-06-06 13:50
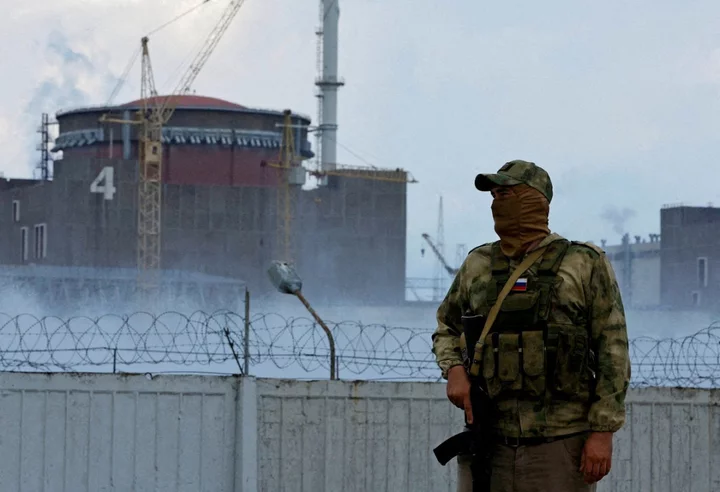

Ukraine-Russia war – live: Putin appoints ‘Grey Hair’ warlord to lead Wagner mercenaries
Andrei Troshev, a founding member and Executive Director of the Wagner Group, reportedly met Valdimir Putin and Deputy Defence Minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov on Thursday night. The meeting underscored the Kremlin’s attempt to show that the state had now gained control over the mercenary group after a failed June mutiny by Wagner chief Yevgeny Prigozhin, who was killed in a plane crash in August. Just days after the Wagner’s mutiny, Putin offered the mercenaries the opportunity to keep fighting but suggested that commander Andrei Troshev take over from Prigozhin, Russia’s Kommersant newspaper has reported. Addressing Troshev, Putin said that they had spoken about how “volunteer units that can perform various combat tasks, above all, of course, in the zone of a special military operation.” “You yourself have been fighting in such a unit for more than a year,” Putin said. “You know what it is, how it is done, you know about the issues that need to be resolved in advance so that the combat work goes in the best and most successful way.” Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told the RIA news agency that Troshev worked at the defence ministry. “He now works in the defence ministry.” Read More Putin’s shameless UN charm offensive - with stolen grain from Ukraine Russian figure skater Kamila Valieva's Olympic doping case will resume for two more days in November Ukraine's Zelenskyy taps celebrities for roles as special adviser and charity ambassador
2023-09-29 14:59
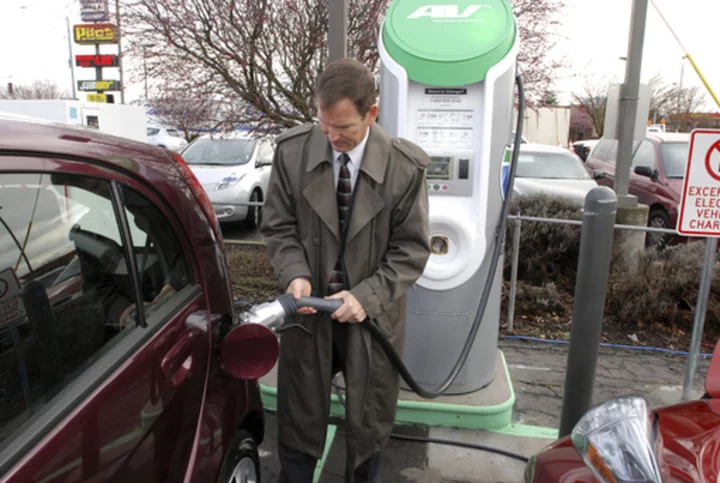

New electric vehicle charging network being built by major automakers could lure more buyers to EVs
The announcement Wednesday that seven automakers will build a large North American electric vehicle charging network should pull people off the sidelines to at least consider switching from gas-powered vehicles
2023-07-27 04:53

Marrakech kicks off film festival in the shadow of war in the Middle East
The Marrakech International Film Festival began on Friday, bringing American and international movie stars to the Arab world as war in the Middle East has led to the cancellation of other film festivals
2023-11-25 04:22

'CBS Mornings' host Tony Dokoupil reveals 'truly horrific' experience his children in Israel went through amid war
Tony Dokoupil said he was 'heartbroken' over the trauma of innocent civilians
2023-10-10 11:18
You Might Like...

Morocco shifts focus to next game after a big loss in its Women's World Cup debut
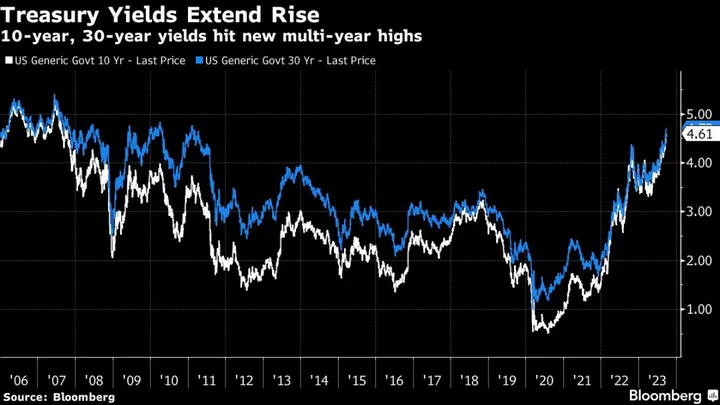
Asian Stocks to Fall, Treasury Yields Extend Rise: Markets Wrap

Fed Chair Powell to give economic outlook at Jackson Hole Aug 25

More than 40 firearms belonging to suspect in Gilgo Beach killings appear to be illegally possessed, prosecutors say
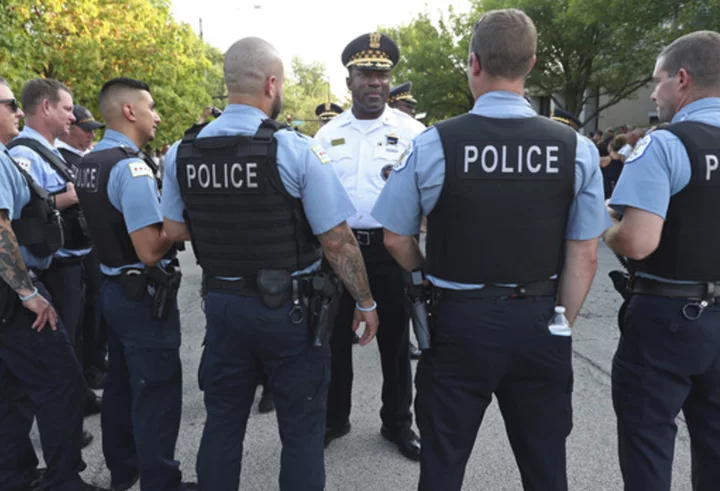

Chicago mayor names the police department’s counterterrorism head as new police superintendent
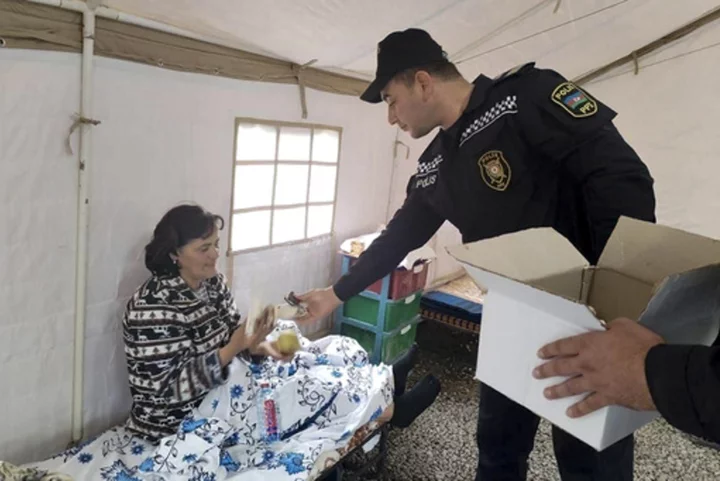

Aid shipments and evacuations as Azerbaijan reasserts control over breakaway province
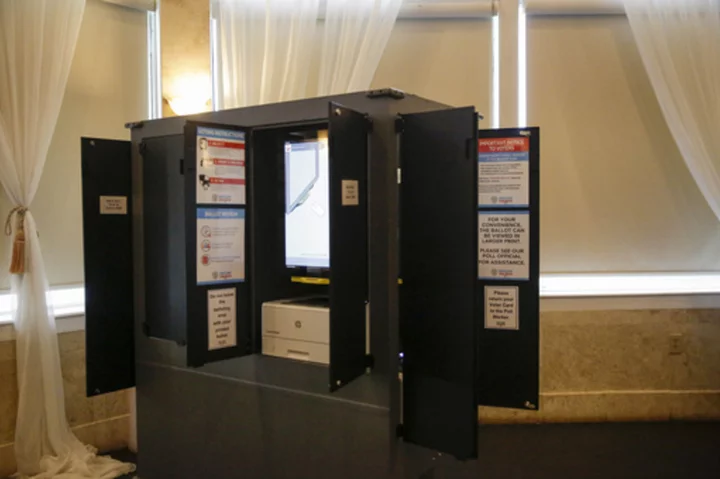

Constitutional challenge to Georgia voting machines set for trial early next year
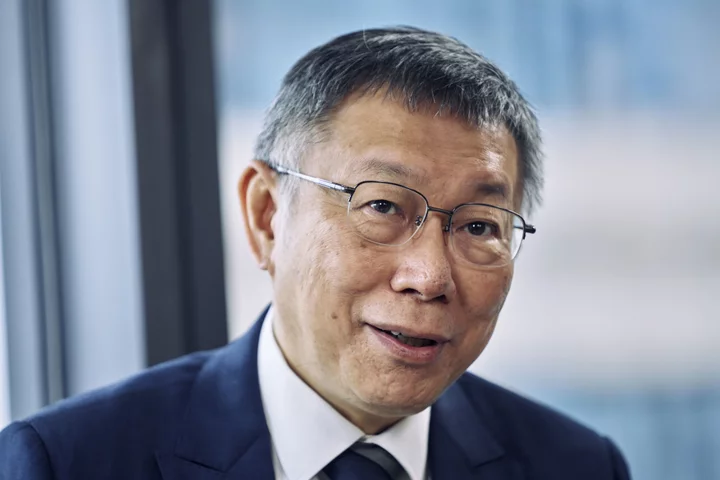

Taiwan Candidate Says He Still Hates Party He’ll Run With
