The world’s most-developed nations will be told to curb their excessive appetite for meat as part of the first comprehensive plan to bring the global agrifood industry into line with the Paris climate agreement.
The global food systems’ road map to 1.5C is expected to be published by the United Nations’ Food & Agriculture Organization during the COP28 summit next month. Nations that over-consume meat will be advised to limit their intake, while developing countries — where under-consumption of meat adds to a prevalent nutrition challenge — will need to improve their livestock farming, according to the FAO.
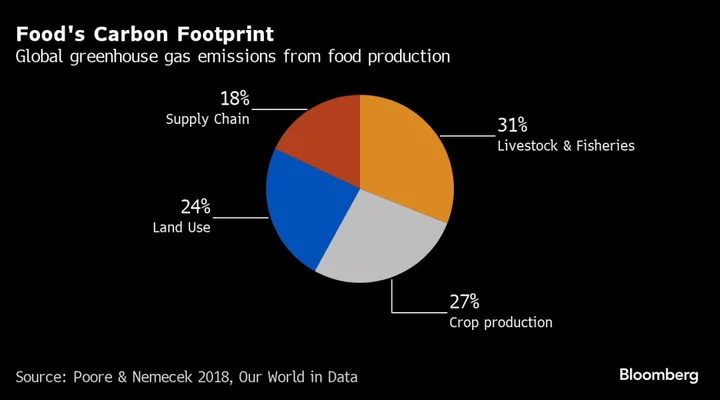
From farm to fork, food systems account for about a third of global greenhouse gas emissions and much of that footprint is linked to livestock farming — a major source of methane, deforestation and biodiversity loss. Although non-binding, the FAO’s plan is expected to inform policy and investment decisions and give a push to the food industry’s climate transition which has lagged other sectors in commitments.
The guidance on meat is intended to send a clear message to governments. But politicians in richer nations typically shy away from policies aimed at influencing consumer behavior, especially where it involves cutting consumption of everyday items.
“Livestock is politically sensitive, but we need to deal with sensitive issues to solve the problem,” said Dhanush Dinesh, the founder of Clim-Eat, which works to accelerate climate action in food systems. “If we don’t tackle the livestock problem, we are not going to solve climate change. The key problem is overconsumption.”
The average American consumes about 127 kilograms of meat a year compared with 7 kilograms in Nigeria and just 3 kilograms in the Democratic Republic of Congo, according to the FAO data. The Eat-Lancet Commission recommends people consume no more than 15.7 kilograms of meat a year.
Read: Rising Livestock Emissions Undermine World’s Climate Fight
The Rome-based UN agency, tasked with improving the agricultural sector and nutrition, is seeking to strike a balance between the climate transition and ensuring food security for the growing global population. So as well as calling for less meat consumption for the world’s well fed, the plan would also encourage farmers in developing countries to bolster productivity of their livestock and supply more sustainably.
Other recommendations will cover issues from how farmers adapt to an increasingly erratic weather to tackling key sources of emissions like food waste and post-harvest loss or fertilizer use, according to the FAO. The plan will be rolled out in three parts over the next few years to eventually include country-specific recommendations.
The road map has the potential to offer a “shared direction of travel” for livestock companies and their investors, mirroring the role of the International Energy Agency’s net zero document for the energy sector, according to FAIRR Initiative, an investor network focused on intensive animal production.
“This road map is needed to bring clarity to both companies and investors so that they can plan for the transition,” said Sofía Condés, head of investor outreach at FAIRR. “The longer companies wait to act, the more drastic and potentially disruptive the transition.”
The FAO’s work is one of several food-focused announcements and pledges that are expected to come out of the COP28 summit in Dubai. While climate summits have tended to steer away from agrifood issues largely due to sensitivities over food security, this year’s organizers are trying to push through a number of initiatives outside the formal talks, said Clim-Eat’s Dinesh.
Read: How to Tell If a Climate Deal Will Succeed or Fail
“I see more people coming, more events, more activities around food systems,” he said.
The United Arab Emirates have called on governments to sign a declaration committing to include food transformation into their national reduction and adaptation plans. The COP28 summit will have a Food, Agriculture and Water Day on Dec. 10, a first-ever day dedicated to food systems, which encompass anything from how food is grown, processed, distributed, consumed or thrown away. Catering for the summit will be two-thirds plant-based.